
Structural features
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
429
الجزء والصفحة:
429
 2025-09-27
2025-09-27
 306
306
Structural features
Metal difluorides, MF2, where M is a Group2 or d-metal, generally adopt the CaF2 or rutile structures and are described well by the ionic model. In contrast, whereas the Group 2 dichlorides, dibromides, and diiodides may be described by the ionic model, the d-metal analogues adopt the CdI2 or CdCl2 layer structures and their bonding is not described well by either the ionic or covalent models. Many metal trifluorides have three-dimensional ionic structures but the trichlorides, tribromides, and triodides have layered structures. The compounds NbF3 and FeF3 (at high temperature) adopt the ReO3 structure type (Section 3.6) and many other metal trifluorides (including AlF3, ScF3, and CoF3) have a slightly distorted variant of this structure type.
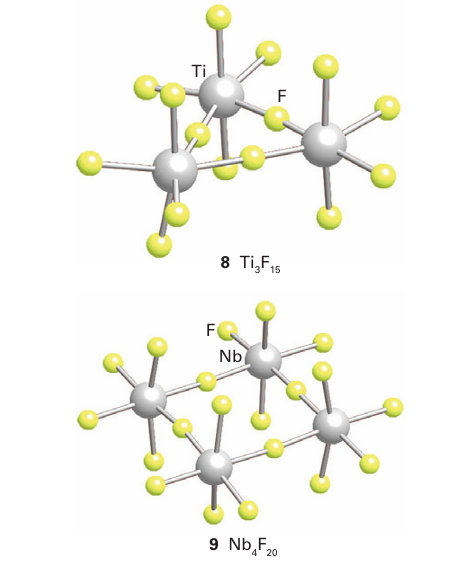
As the oxidation number of the metal atom increases, the halides become more covalent. Thus, all metal hexahalides such as MoF6 and WCl6, are molecular covalent compounds. For inter mediate oxidation states (such as MF4 and MF5) the structures normally consist of linked MF6 polyhedra. Titanium tetrafluoride has a structure based on columns of triangular Ti3 F15 units formed from three TiF6 octahedra (8) whereas NbF5 is built from four NbF6 octahedra forming a square unit of composition Nb4F20 (9).
Although not as important in applications as complex ox ides, complex solid fluorides and chlorides such as the ternary phases MMFn and MM’Cln , and the quaternary compounds MM’M’’Fn, have structures similar to their oxide counterparts. As F has an oxidation number of 1 compared to 2 for O2 -, the compositionally equivalent fluorides or chlorides generally contain d metals in lower oxidation states than the equivalent oxide. Thus, ternary fluorides of stoichiometry ABF3 with, for example, A=K, Rb, and Cs and M a dipositive d-metal ion, adopt the perovskite structure (Section 3.9). One example is KMnF3, which precipitates when potassium fluoride is added to Mn (II) solutions. Molten cryolite, Na3 AlF6, is used to dissolve aluminium oxide in electrochemical extraction of aluminium. Its structure is related to that of perovskite (ABO3) with Na in the A sites and a mixture of Na and Al in the B sites: the formula Na (Al½ Na½) F3, which is equivalent to Na3AlF6. Mixed-anion compounds containing halides are also well characterized and include the superconducting cuprate Sr2-x Nax CuO2F2.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


