
Metal oxides
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص460-461
الجزء والصفحة:
ص460-461
 2025-09-24
2025-09-24
 294
294
Metal oxides
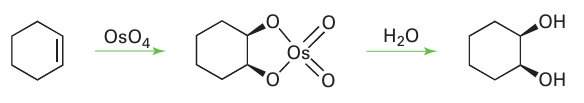
Key point: Many different oxides of the d-block elements exist, with a wide variety of structures, varying from ionic lattices to covalent molecules. Many different oxides are known for the d-block elements, with a number of different structures. We have already noted the ability of oxygen to bring out the highest oxidation state for some elements, but oxides exist for some elements in very low oxidation states: in Cu2O, copper is present as Cu(I). Monoxides are known for all of the 3d-series metals, except Cr. The monoxides have the rock-salt structure characteristic of ionic solids but their properties, indicate significant deviations from the simple ionic M2O2 model. For example, TiO has metallic conductivity and FeO is always deficient in iron. The early d-block monoxides are strong reducing agents. Thus, TiO is easily oxidized by water or oxygen, and MnO is a convenient oxygen scavenger that is used in the laboratory to remove oxygen impurity in inert gases down to the parts-per-billion range. As we have already noted, very high oxidation state oxides can show covalent structures. For example ruthenium tetroxide and osmium tetroxide are low melting, highly volatile, toxic, molecular compounds that are used as selective oxidizing agents. Indeed, osmium tetroxide is used as the standard reagent to oxidize alkenes to cis-diols:
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


