
Boron oxygen compounds
 المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
 المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
 الجزء والصفحة:
ص334-335
الجزء والصفحة:
ص334-335
 2025-08-31
2025-08-31
 361
361
Boron oxygen compounds
Key point: Boron forms B2O3, polyborates, and borosilicate glasses. Boric acid, B(OH)3, is a very weak Brønsted acid in aqueous solution. However, the equilibria are more complicated than the simple Brønsted proton transfer reactions characteristic of the later p-block oxoacids. Boric acid is in fact primarily a weak Lewis acid, and the complex it forms with H2O, H2OB(OH)3 , is the actual source of protons:
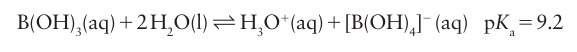
As is typical of many of the lighter elements of the p block, there is a tendency for the anion to polymerize by condensation, with the loss of H2O. Thus, in concentrated neutral or basic solution, equilibria such as
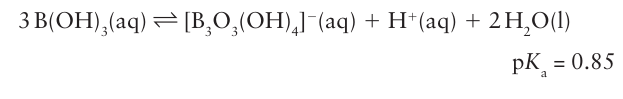
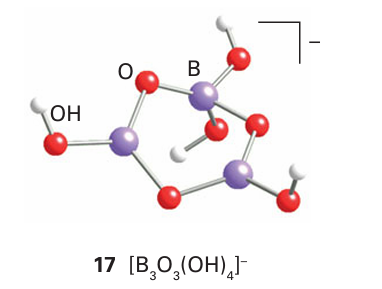
occur to yield polynuclear anions (17).
The reaction of boric acid with an alcohol in the presence of sulfuric acid leads to the formation of simple borate esters, which are compounds of the form B(OR)3:
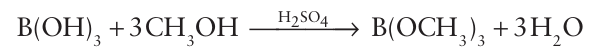
Borate esters are much weaker Lewis acids than the boron tri halides, presumably because the O atom acts as an intramolecular π donor, like the F atom in BF3 (Section 4.10b), and donates electron density to the p orbital of the B atom. Hence, judging from Lewis acidity, an O atom is more effective than an F atom as a π donor towards B. 1,2-Diols have a particularly strong tendency to form borate esters on account of the chelate effect (Section 20.1), and produce a cyclic borate ester (18).
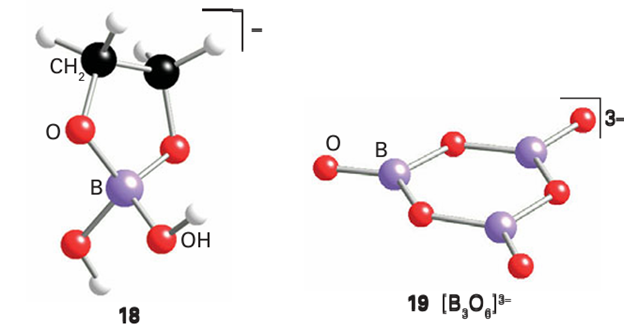
As with silicates and aluminates, there are many polynuclear borates, and both cyclic and chain species are known. An example is the cyclic polyborate anion B3O6-3 (19). A notable feature of borate formation is the possibility of both three-coordinate B atoms, as in (19), and four-coordinate B atoms, as in [B(OH)4]. Polyborates form by sharing one O atom with a neighbouring B atom, as in (19); structures in which two adjacent B atoms share two or three O atoms are unknown. Boron oxide, B2O3, is acidic and is prepared by dehydration of boric acid:
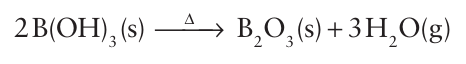
The rapid cooling of molten B2 O3 or metal borates often leads to the formation of borate glasses. Although these glasses themselves have little technological significance, the fusion of sodium borate with silica leads to the formation of borosilicate glasses (such as Pyrex). Borosilicate glasses are resistant to thermal shock and can be heated over a flame or other source of direct heat. Sodium perborate is used as a bleach in laundry powders, automatic dishwasher powders, and whitening toothpastes. Al though the formula is often given as NaBO3.4H2O, the com pound contains the peroxide anion, O22- , and is more accurately described as Na2[B2(O2)2(OH)4].6H2O. The compound is pre ferred to hydrogen peroxide in many applications because it is more stable and liberates oxygen only at elevated temperatures.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


