

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Implementation and methodology
المؤلف:
Neil James & Mike Miles & Cheryl Burton & Chris Ricketts
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P178-C16
2025-07-02
565
Implementation and methodology
Success in a developmental project of this nature requires close liaison between module leader and lecturing staff, students, and the person responsible for implementing the bespoke computer systems and digital media necessary to support CAPA. In this trial, the bespoke systems included adaptations of parts of the MLE. This required significant manual intervention and liaison with IT support staff. A unique aspect of this trial was that the only constraints on the format of the file submitted by the students were: i) it had to be a single Word document but any facility or attribute within Word was allowed; ii) it had to be less than 5Mb in size. Most other similar methods utilize submission from a screen into a text box of unformatted text.
James, M.N. (2005) provides a link to the web resources that were provided for engineering design students during this project. It is intended that this module (Design as a Generic Tool) uses web-based material both to support self-learning and the lecture program; and CAPA represents a logical extension to this student centred learning environment (Atsusi Hirumi, 2005). The CAPA resources on this web site indicate the additional support necessary to enable the majority of students to successfully complete all the steps of the assignment.
The initial step in the CAPA process was to persuade students to register with the University Computer Service to get a user name and password. After four weeks of repeating this point in lectures and emphasizing that module resources were linked from the student portal (the login homepage) and that the assignment could not be done without completing registration, some students had still not attempted this process. In certain cases, the underlying reasons appeared to be inadequate knowledge of campus layout, coupled with cultural difficulties around acknowledging incomplete understanding of the task. This is mentioned as a reminder that what seem to be simple points can create major problems for individual students.
Critical steps in the implementation include:
1. Training students so that they understand assessment criteria and grade descriptors
This was done by providing examples of marked and annotated assessed work submitted by students in previous years. These were provided in advance of the assignment submission date as anonymized online Adobe Acrobat files demonstrating excellent, satisfactory and unsatisfactory assignments. Marking of the assignments was to be done online in the MLE using a template produced with Question mark Perception software. Rather than expecting students to mark holistically, a set of 12 assessment criteria was developed. These criteria covered both the design and engineering content and the presentation of the report. A set of generic grade descriptors was developed which could be applied to each criterion. Full details can be found at (James, 2005). This marking template was provided in advance of the assignment submission date, and contained the description of grade classifications and the twelve criteria against which the essay was to be marked.
It also demonstrated typical feedback to the student and introduced the concept of a 'criticism sandwich' (Dohrenwend, 2002), where a specific criticism is 'sandwiched' between two specific praises. Students were encouraged to give written feedback to help other students improve. The marking template included the rubric "Your feedback, which is very important, should be a minimum of 30 words identifying the strengths and weaknesses of this piece of work. Any suggestions on how it might be improved would be welcomed. Put yourself in the place of the student whose report you are marking would you appreciate and learn from the feedback you are giving". These resources were introduced and discussed in class. If this training was assimilated by students, they would be equipped to understand the assessment requirements and produce a high-quality assessment themselves.
2. Discussing fully the system of allocating marks in the assignment with the students during class and clearly answering their questions
Each submitted assignment would be automatically distributed on-line to three other randomly chosen students. The mark allocated to the assignment would be the average of all three, and the student would receive three pieces of feedback. Students who failed to complete the marking would lose one-third of their own marks for each unmarked assignment. Thus not marking any assignments, even if an assignment was submitted, would yield a zero mark. In the event, this strategy achieved a highly successful marking outcome. In the first year design module, for example, 82% of 145 students marked all 3 essays and only two students marked < 2 essays. The final withdrawal rate from this module was 3% (5 students). Only two possible cases of plagiarism were noted by the markers and one of these cases was upheld on examination by lecturing staff.
3. Agreeing criteria for staff sampling of assessed work to generate confidence in results
A minimum of 10% of the essays would be sampled by staff. This sample would generally be randomly chosen but would include those where the average mark lay on a classification boundary (e.g. between 1st /2nd); failing assessments and cases of suspected plagiarism; cases where there was a large variation between assessors marks; and cases where the essay was marked by < 2 students. In practice 23% of essays fell within one of these categories, with the largest categories being those of 'classification boundary' (10%) and 'failing' (6%).
A very small number of complaints about mark allocation were recorded and the results obtained by the students in this assignment are shown in the bar chart in Figure 1.
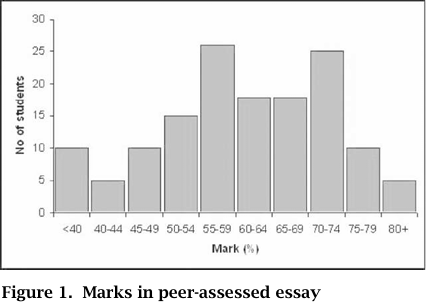
The three marks for each essay were ranked from highest to lowest, and the mean difference between any two neighboring marks was 9.6 with a standard deviation of 7.5. The mean difference between the highest and lowest marks for individual students was 18.8 with a standard deviation of 9.9. Whilst these differences might seem relatively large, in the essays sampled the average values were generally close to the mark that lecturing staff would have awarded.
In the smaller engineering management group all scripts were checked by the lecturer and the average marks given by the students were within approximately 10% of those that he would have awarded.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















