

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Semantic blocking
المؤلف:
Andrew Carstairs-McCarthy
المصدر:
An Introduction To English Morphology
الجزء والصفحة:
91-8
2024-02-05
2241
Semantic blocking
The pattern of semantic relationships exhibited at (2) illustrates a further point about the way in which meaning interacts with derivation. Why are there no words such as ‘cowlet ’ and ‘sheepling’, formed with the same suffixes as piglet and gosling, and with corresponding meanings? Intuitively, one feels that it has something to do with the fact that the words calf and lamb exist, with exactly the meanings that ‘cowlet ’ and ‘sheepling’ would have. But that would work as an explanation only if the existence of exact synonyms is, for some reason, not tolerated or at least discouraged. Is there any evidence for that?
At first sight, pairs of exact synonyms are easy to find: courgettes and zucchini, for example, or despise and scorn, or nearly and almost. But on closer examination one finds either that the words in each pair belong to different dialects, or that they are not after all completely interchangeable. Thus, zucchini is used in the USA while courgettes is more general in Britain; Bill scorned our apology implies that Bill rejected it, whereas Bill despised our apology means rather that he despised us for offering it; and one cannot substitute almost for nearly in the phrase not nearly meaning ‘far from’, as in I’m not nearly ready yet. What’s more, from research into the acquisition of vocabulary in early childhood, we know that children assume that every new word means something new, and is not merely an alternative for a word already learned. So our intuition that calf and lamb somehow ‘block’ ‘cowlet ’ and ‘sheepling’ is supported by evidence. Let us define semantic blocking as the phenomenon whereby the existence of a word (whether simple or derived) with a particular meaning inhibits the morphological derivation, even by formally regular means, of another word with precisely that meaning.
For a nice illustration of the operation of semantic blocking, consider the nouns corresponding to the adjectives curious and glorious. The suffix -ous yields a formally regular base for the suffixation of -ity, so we might expect the corresponding nouns to be curiosity and ‘gloriosity’. In fact, curiosity is in regular use but ‘gloriosity’ is not. The reason is that ‘gloriosity’ is blocked semantically by the noun glory, which (so to speak) pre-empts the relevant meaning. On the other hand, there is no noun such as ‘cury’ that might block the derivation of curiosity from curious.
For a further illustration, consider a set of nouns that correspond to verbs expressing emotional attitude:
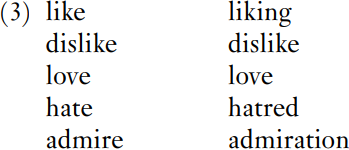
The nouns are formed in a variety of ways, including conversion, but semantically they are regular. What of the verb despise, however? We might expect to find a suffixally derived noun to correspond to it, such as ‘despisement ’ or ‘despisal ’. But these are blocked by the noun contempt, which stands in the same semantic relationship to despise as admiration does to admire. The relationship between despise and contempt looks rather like the relationship in inflectional morphology between go and went, which we called ‘suppletive’. However, there is an important difference: go and went are morphologically related, despite their lack of a shared root, in that they are forms of the same lexeme, like organize and organized; on the other hand, despise and contempt belong to different lexemes, so their lack of a shared root means that there is no morphological relationship between them at all, except indirectly through blocking. The same sort of reason can plausibly be invoked to explain why an adjective such as ‘ungood ’ does not exist, even though un-is formally and semantically so general: it is blocked by bad, with which it would be exactly synonymous, just as ‘unlong’ would be synonymous with short, ‘unhot ’ with cold, and so on.
According to the definition of semantic blocking, even a formally regular process can be blocked. As an illustration, consider the formation of adverbs in -ly from adjectives, as in quickly and slowly. This a formally regular and general process; even so, the idiosyncratic existence of an adverb without -ly may block it, as with the adjective fast, whose corresponding adverb is simply fast, not ‘fastly’. Likewise, the semantically regular abstract noun corresponding to high is height, which blocks the use of highness in this sense. However, highness (unlike ‘fastly’) exists because it has acquired a technical metaphorical sense in expressions such as Your Royal Highness.
In inflectional morphology, the blocking effect of suppletion is absolute. The existence of went means that *goed will never be used, unless by a young child or an adult learner. Derivational morphology, however, is less tightly structured than inflectional, so semantic blocking can be a matter of degree. Just as formally regular ‘longness’ seems less odd than irregular *greyth, so gloriousness with its highly general suffix sounds more natural than ‘gloriosity’ with its less general one. The blocking effect of glory has to compete with the regularity and generality of -ness suffixation, and may not always win. Even so, if we encounter gloriousness, we expect its use to be differentiated, even if only minimally, from that of glory.
 الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















