

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Identifying morphemes independently of meaning
المؤلف:
Andrew Carstairs-McCarthy
المصدر:
An Introduction To English Morphology
الجزء والصفحة:
23-3
2024-01-31
1886
Identifying morphemes independently of meaning
A somewhat different kind of lexical conditioning can be introduced by means of the prefix re- and its possible allomorphs. This prefix can be added to verbs quite freely, contributing the meaning ‘again’, as in rewrite, reread, repaint, revisit. In these words the prefix has a vowel rather like that of see, and can be represented phonetically as [ri]. But something that looks very much like the same prefix occurs also in verbs such as revive, return, restore, revise, reverse, this time pronounced with a so-called ‘reduced vowel’, [rI] or [rə]. What’s more, many of these words have a meaning in which it is possible to discern an element such as ‘again’ or ‘backward movement’: for example, revive means ‘bring back to life’, return means ‘come back’ or ‘give back’, restore means ‘bring back to a former condition’, and revise means ‘look at again, with a view to changing’. It may therefore seem natural to treat [ri] and [rə] as allomorphs of the same morpheme.
A snag, however, is that there are some roots with which both [ri] and [rə] can occur, yielding different meanings: for example, the meanings just given for restore and return are distinct from those for re-store ‘store again’ and re-turn ‘turn again’ (as in I turned the steaks on the barbecue a minute ago, and I’ll re-turn them soon). The [ri] prefix can be added to almost any verb, with the consistent meaning ‘again’, whereas the [rə] prefix is lexically much more restricted as well as harder to pin down semantically. One must conclude that the two prefixes pronounced [ri] and [rə] belong to distinct morphemes in modern English, their phonetic and semantic similarities being due to their having the same historical source in that part of English vocabulary that has been borrowed from Latin via French.
As an alternative to that conclusion, one might consider rejecting the analysis of revive, return, restore, revise and reverse as consisting of a prefix plus a root, and instead treat them as monomorphemic. But this has unwelcome consequences too. If revive and revise are single morphemes, that amounts to saying that they have no parts in common (except phonologically) with survive and supervise. But that is unwelcome, because it inhibits us from recognizing sur- and super- as morphemes that recur in surpass and superimpose. In fact, many English words (mainly verbs and words related to them) form a complex network, with what looks like a prefix–root structure (the root being usually bound), but without any clear consistent meaning being ascribable to either the prefix or the root. Here is just a small part of that network:

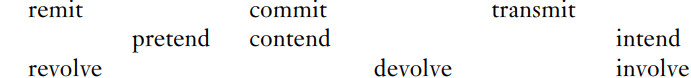
If we adhere strictly to the view that individual morphemes must be meaningful, then all these words must seemingly be treated as mono-morphemic; for no consistent meaning can be identified in modern English for any of the purported morphemes that they contain (for example, no element such as ‘backward movement’ or ‘again’ can be plausibly discerned within the meaning of reserve). But a consideration of allomorphy shows that that would be unsatisfactory. If reduce, conduce, deduce and induce have no morpheme in common, then the fact that for all of them there is a corresponding noun in which -duce is replace with -duct- (reduction, conduction etc.) seems to be a pure accident. However, this shared pattern of allomorphy is just what we expect if -duce is a root morpheme that they all share (one of its allomorphs being -duct-), while they differ prefixally. A similar point can be made about the nouns revolution, devolution and involution related to revolve, devolve and involve: again, an unusual pattern of allomorphy makes sense if the same root morpheme is contained in all these words (-volve, with allomorph -volu-), but it makes no sense if these words have no more in common than e.g. loaf and oaf.
Some of the nouns and verbs that I have just claimed to be related do not have much to do with each other semantically, one must admit. For example, the meaning of conduce (a rather rare verb) has nothing to do with that of conduction, and the noun that seems most closely related to involve is not involution (another rarity) but involvement. However, that just confirms a central characteristic of these prefix–root combinations: the prefixes and roots that they comprise are identifiable without reference to meaning. Because of this, all these complex words must clearly be lexical items. Thus the lexical conditioning to which these morphemes are subject is of a particularly strong kind: none of them ever occurs except in complex words that require dictionary listing.
The idea that these morphemes occur only in words that are lexical items fits nicely a salient characteristic of the table at (2), namely its ‘gappiness’. A list of lexical items is essentially arbitrary; therefore one will not expect to be able to predict confidently that any one conceivable prefix–root combination will be present in the list. For example, nothing guarantees that there should be a word such as ‘transvoke’ or ‘premit ’ – and indeed there is not (at least in the ordinary vocabulary of modern English speakers). Two of the gaps in (2) might be filled if we allowed as fillers not just verbs but other words related to them: for, even though ‘transduce’ and ‘convolve’ do not exist, we can find transducer, convolution and convoluted in any dictionary. It may seem at first paradoxical that these other words should exist while the verbs from which they are formed, in some sense (the sense in which e.g. helpful is ‘formed from’ help), do not exist. Again, however, this ceases to be surprising if the Latin-derived prefixes and roots that we have been considering have so extensively lost any clearly identifiable meanings as to enforce lexical listing for all words formed with them.
 الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
الاكثر قراءة في Morphology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















