
Structure of the Alkyl Group, R, in SN2 Reactions
 المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
المؤلف:
John D. Roberts and Marjorie C. Caserio
 المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
المصدر:
Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry : LibreTexts project
 الجزء والصفحة:
........
الجزء والصفحة:
........
 5-1-2022
5-1-2022
 2443
2443
Structure of the Alkyl Group, R, in SN2 Reactions
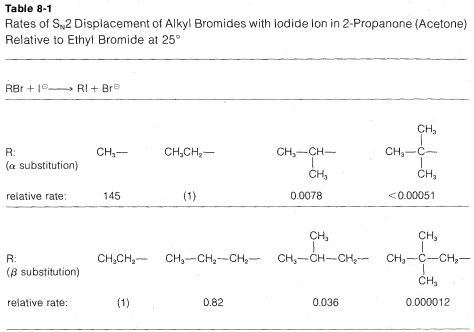
The rates of SN2-displacement reactions of simple alkyl derivatives, RX, follow the order primary R >> secondary R ≫ tertiary R. In practical syntheses involving SN2 reactions, the primary compounds generally work very well, secondary isomers are fair, and the tertiary isomers are almost completely impractical. Steric hindrance appears to be particularly important in determining SN2 reaction rates, and the slowness of tertiary halides seems best accounted for by steric hindrance to the back-side approach of an attacking nucleophile by the alkyl groups on the reacting carbon. Pertinent data, which show how alkyl groups affect SN2 reactivity toward iodide ion, are given in Table 8-1. Not only do alkyl groups suppress reactivity when on the same carbon as the leaving group X, as in tert-butyl bromide, but they also have retarding effects when located one carbon away from the leaving group. This is evident in the data of Table 8-1 for 1-bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane (neopentyl bromide), which is very unreactive in SN2 reactions. Scale models indicate the retardation to be the result of steric hindrance by the methyl groups located on the adjacent β carbon to the approaching nucleophile:
In addition to steric effects, other structural effects of RR influence the SN2 reactivity of RX. A double bond β to the halogen,6 as in 2-propenyl, phenylmethyl (benzyl), and 2-oxopropyl chlorides enhances the reactivity of the compounds toward nucleophiles. Thus the relative reactivities toward I⊖ in 2-propanone are
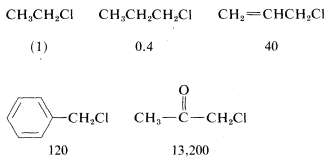
Possible reasons for these high reactivities will be discussed later.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


