

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Parathyroid glands
المؤلف:
Kelly M. Harrell and Ronald Dudek
المصدر:
Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
1-8-2021
2784
Parathyroid glands
Superior and inferior parathyroid glands are typically located bilaterally on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland . Multiple in number, these small, oval glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH), which regulates phosphorus and calcium metabolism in the bloodstream.
1. Vasculature and lymphatics: The main blood supply to the parathyroid glands is by way of the inferior thyroid artery, although surrounding arterial supply can also contribute depending on the exact location. Parathyroid veins drain the glands, and lymphatic drainage communicates with that of the thyroid gland. Also, like the thyroid gland, the parathyroid glands are regulated hormonally. Nerves arising from the cervical sympathetic ganglia carry a vasomotor function, but do not control gland function.
2. Histology: The parathyroid glands are yellow to orange tan in color (depending on the amount of stromal fat). Most individuals have four parathyroid glands, but the number may vary from 1 to 12. They measure about 4 mm wide by 6 mm long by 4 mm thick. The shape of the parathyroid glands varies because the glands are molded by adjacent anatomical structures. Each parathyroid gland is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule that sends connective tissue septae into the parathyroid gland for support. The parathyroid glands contain two types of cells: chief cells and oxyphil cells.
a. Chief cell: Chief cells are polygon-shaped cells with a round, centrally located nucleus (Fig. 1). They contain rough endoplasmic reticulum, polyribosomes, a Golgi complex, mitochondria, secretory granules, lipid, and glycogen. The chief cell secretes PTH that binds to the PTH receptor (a G protein-linked receptor). PTH is involved in calcium homeostasis (i.e., raises blood calcium levels).
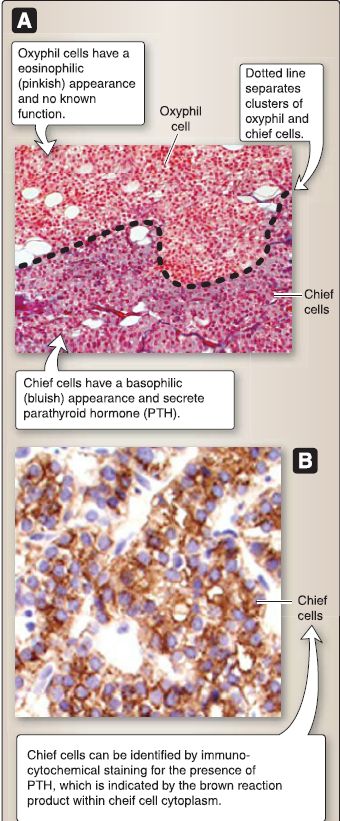
Figure 1: Parathyroid histology. A, Mallory trichrome stain. B, Anti-parathyroid hormone/diaminobenzidene stain.
b. Oxyphil cell: Oxyphil cells appear after puberty and have a distinct eosinophilic cytoplasm because of numerous mitochondria. The cell has no known function.
c. Weight: The weight of the parathyroid glands is an important parameter in histopathologic assessment. All parathyroid glands (or parts of parathyroid glands) must be carefully weighed. Each parathyroid gland weighs about 35-40 mg. The total parathyroid weight ranges from 120 to 140 mg.
 الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
الاكثر قراءة في علم التشريح
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















