

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Imaginary Condition
المؤلف:
PREPLY.COM
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
15-6-2021
2392
5 Types of Conditional Sentences in English (+ Examples)
Conditional sentences are one of the trickier parts of English grammar: there are 5 types of conditional sentences, and you need to be able to use and identify all of them. As a rule, conditional sentences in English consist of two parts – the main part and the if part (or the conditional part).
These types of sentences are used to express possible or imaginary situations.
The order of these two parts of the sentence isn’t important.
When written, if the if part of the sentence comes first, a comma should be used to separate it from the second part.
5 Types of Conditional Sentences
Before we get started, here’s a brief chart summarizing the 5 types of conditional sentences and how they’re used:
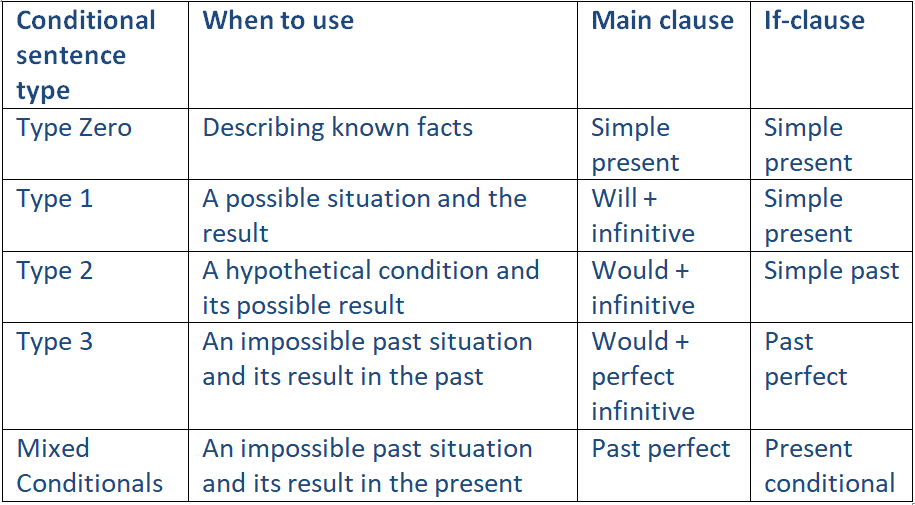
Type Zero Conditional Sentences (zero condition)
This type of conditional sentence is used to describe scientific facts, generally known truths, events and other things that are always true.
I think it’s the simplest type of conditional sentence in English.
The structure of Type Zero conditional sentences:
Main part: Present Simple; if part: Present Simple
Examples:
Water boils if you heat it to 100 degrees Celsius.
A red light comes on if you press the main button.
In Type Zero sentences, if can be replaced by when.
Examples:
When you heat ice, it melts.
It gets dark when the sun goes down.
Type One Conditional Sentences (open condition)
This type of sentence expresses real and possible situations in the future; it is possible for the condition to be met.
The structure of Type One conditional sentences:
Main part: will + infinitive; if part: Present Simple
Examples:
We will stay at home if it snows.
She will get angry if I‘m late for the party.
If we get the money for this job, we will buy a new car.
Will you help Amanda if she asks you?
Type Two Conditional Sentences (half-open condition)
This type of conditional sentence describes an unreal situation with regard to the present or future; a hypothetical condition that can only be fulfilled in theory.
The structure of Type Two conditional sentences:
Main part: would + infinitive; if part: Past Simple
In conditional sentences, the past tense form of the verb to be is were for all persons; was is also used, although only in spoken or conversational English.
Examples:
We would stay at home if it snowed.
I would buy a new board if I had more money.
If he were rich, he‘d buy an island.
If you left now, you‘d catch the last bus.
The phrases If I were you or If I were in your place are usually used to give advice.
Examples:
If I were you I would accept the offer.
If he were in your place he would do it.
Type Three Conditional Sentences (closed condition)
Type three conditional sentences are used to express situations that cannot exist, such as actions or events that happened in the past. They are often used to indicate a missed opportunity.
The structure of Type Three conditional sentences:
Main part: would + perfect infinite; if part: Past Perfect
Examples:
If you hadn’t been late for work, the boss wouldn’t have gotten furious.
They would have finished earlier if the meeting hadn’t been held so late.
If I had won the lottery, I would have bought a house by the sea.
Would you have helped me if I had asked you?
Mixed Conditionals
This type of conditional sentence uses (mixes) different parts of the above-mentioned conditional sentence types.
There are a few combinations: the condition emphasizes the result of the action in the present in the past tense, or the present-day condition emphasizes the result of the action in the past.
Examples:
If you had taught me how to make waffles (in the past), I wouldn’t have to buy them in a shop (now).
I would buy a house by the sea (now or in the future) if I had won the lottery last week.
Their team would have scored more in the match yesterday if they were good players.
Important Grammatical Notes
If the modal verbs can/could, may/might or should are used in the main part of the sentence, they take the place of will:
We can go to the seaside if you have time tomorrow.
If you leave now, you may catch the last bus.
If you want to pass the exam, you should study much harder.
The words will and would are not usually used in the if part, except when they express willingness, for example, in requests (that is, when they carry a modal meaning):
If you will phone the manager now, he will surely make an appointment with you. (willingness)
I would be very thankful if you would help me with my homework. (very polite request)
The word should in the if part can mean “if perhaps” or “by any chance.”
I would be very happy if he should turn up at the party. (He’s not at all likely to come, but perhaps…)
In negative sentences, if…not can be substituted with unless.
You won’t pass the exam unless you study very hard. (= if you don’t study very hard)
If can be omitted from the sentence if the word order is changed. This is sometimes done in Type Three conditional sentences if the, if part is at the beginning of the sentence, or in Type Two sentences if the verb were, is used:
Were I rich, I would buy a house by the sea. (= if I were rich)
Had your cousin come earlier, I would have shown her around the house. (= if she had come earlier)
 الاكثر قراءة في Imaginary condition
الاكثر قراءة في Imaginary condition
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















