

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Past Simple
المؤلف:
EF.COM
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
29-3-2021
1160
Simple past tense
Definition of the simple past tense
The simple past tense, sometimes called the preterit, is used to talk about a completed action in a time before now. The simple past is the basic form of past tense in English. The time of the action can be in the recent past or the distant past and action duration is not important.
Examples:
John Cabot sailed to America in 1498.
My father died last year.
He lived in Fiji in 1976.
We crossed the Channel yesterday.
You always use the simple past when you say when something happened, so it is associated with certain past time expressions
frequency: often, sometimes, always
I sometimes walked home at lunchtime.
I often brought my lunch to school.
a definite point in time: last week, when I was a child, yesterday, six weeks ago
We saw a good film last week.
Yesterday, I arrived in Geneva.
She finished her work at seven o'clock
I went to the theatre last night
an indefinite point in time: the other day, ages ago, a long time ago
People lived in caves a long time ago.
She played the piano when she was a child.
Note: the word ago is a useful way of expressing the distance into the past. It is placed after the period of time: a week ago, three years ago, a minute ago.
Be Careful: The simple past in English may look like a tense in your own language, but the meaning may be different.
Forming the simple past tense
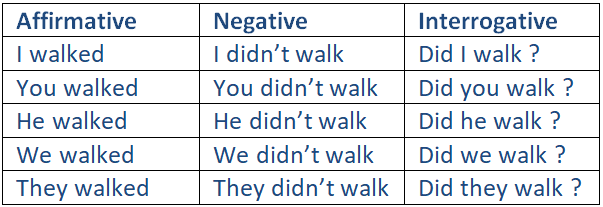
Patterns of simple past tense for regular verbs
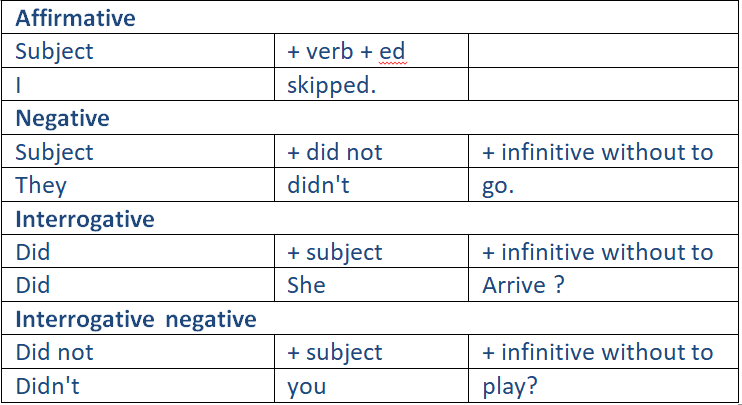
To Walk
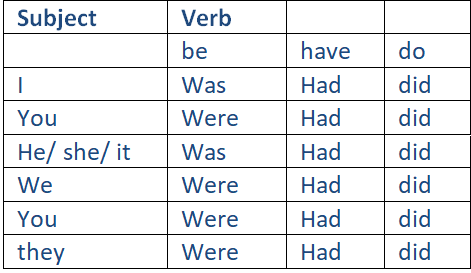
Simple past tense of to be, to have, to do
Notes on affirmative, negative, & interrogative forms
Affirmative
The affirmative of the simple past tense is simple.
I was in Japan last year
She had a headache yesterday.
We did our homework last night.
Negative and interrogative
For the negative and interrogative simple past form of "to do" as an ordinary verb, use the auxiliary "did", e.g. We didn't do our homework last night.
The negative of "have" in the simple past is usually formed using the auxiliary "did", but sometimes by simply adding not or the contraction "n't".
The interrogative form of "have" in the simple past normally uses the auxiliary "did".
Examples :
They weren't in Rio last summer.
We didn't have any money.
We didn't have time to visit the Eiffel Tower.
We didn't do our exercises this morning.
Were they in Iceland last January?
Did you have a bicycle when you were young?
Did you do much climbing in Switzerland?
Note: For the negative and interrogative form of all verbs in the simple past, always use the auxiliary 'did''.
Simple past, irregular verbs
Some verbs are irregular in the simple past. Here are the most common ones.
to go
He went to a club last night.
Did he go to the cinema last night?
He didn't go to bed early last night.
to give
We gave her a doll for her birthday.
They didn't give John their new address.
Did Barry give you my passport?
to come
My parents came to visit me last July.
We didn't come because it was raining.
Did he come to your party last week?
 الاكثر قراءة في Past Simple
الاكثر قراءة في Past Simple
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















