

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Names and Properties of Alkyl Halides
المؤلف:
..................
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
23-7-2019
1044
Names and Properties of Alkyl Halides
- write the IUPAC name of a halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbon, given its Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure.
- draw the Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure of a halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbon, given it IUPAC name.
- write the IUPAC name and draw the Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure of a simple alkyl halide, given a systematic, non-IUPAC name (e.g., sec-butyl iodide).
- arrange a given series of carbon-halogen bonds in order of increasing or decreasing length and strength.
* Notes
This section contains little that is new. If you mastered the IUPAC nomenclature of alkanes, you should have little difficulty in naming alkyl halides. Notice that when a group such as CH2Br must be regarded as a substituent, rather than as part of the main chain, we may use terms such as bromomethyl.
You will find it easier to understand the reactions of the alkyl halides if you keep the polarity of the C−X
- write the IUPAC name of a halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbon, given its Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure.
- draw the Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure of a halogenated aliphatic hydrocarbon, given it IUPAC name.
- write the IUPAC name and draw the Kekulé, condensed or shorthand structure of a simple alkyl halide, given a systematic, non-IUPAC name (e.g., sec-butyl iodide).
- arrange a given series of carbon-halogen bonds in order of increasing or decreasing length and strength.
* Notes
This section contains little that is new. If you mastered the IUPAC nomenclature of alkanes, you should have little difficulty in naming alkyl halides. Notice that when a group such as CH2Br must be regarded as a substituent, rather than as part of the main chain, we may use terms such as bromomethyl.
You will find it easier to understand the reactions of the alkyl halides if you keep the polarity of the C−X
bond fixed permanently in your mind (see ”The Polar C− X Bond” shown in the reading below).
Alkyl halides are also known as haloalkanes. This page explains what they are and discusses their physical properties. alkyl halides are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by halogen atoms (fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine). We will only look at compounds containing one halogen atom. For example:
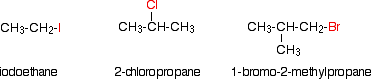
alkyl halides fall into different classes depending on how the halogen atom is positioned on the chain of carbon atoms. There are some chemical differences between the various types.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















