
Visualization and comparison with a ‘Newtonian’ star
 المؤلف:
Heino Falcke and Friedrich W Hehl
المؤلف:
Heino Falcke and Friedrich W Hehl
 المصدر:
THE GALACTIC BLACK HOLE Lectures on General Relativity and Astrophysics
المصدر:
THE GALACTIC BLACK HOLE Lectures on General Relativity and Astrophysics
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 27
الجزء والصفحة:
p 27
 23-1-2017
23-1-2017
 2319
2319
Visualization and comparison with a ‘Newtonian’ star
From the continuous matching of the grr-component we can derive the relation 1 − 2m/Rּ = 1 − R2ּ/ ˆR2. Together with the definition of the Schwarzschild radius we find for the total gravitating mass of the star
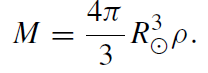 (1.1)
(1.1)
Another method for obtaining the total mass is to multiply the density ρ by the spatial volume of the star at a given time t0. However, the total mass calculated that way is larger than the total gravitating mass (1.1). This is due to the fact that not mass (that is ‘rest mass’) alone but mass-energy gravitates. The negative gravitational binding forces thus contribute to the gravitating mass which appears in the metric.
Finally, some words about the geometry of the Schwarzschild spacetime. We can visualize its structure by means of an embedding in the following way: In the equatorial plane ϑ = π/2 at a prescribed time t = t0, the metric reads ( ˆR 2 = R3ּ /2m):
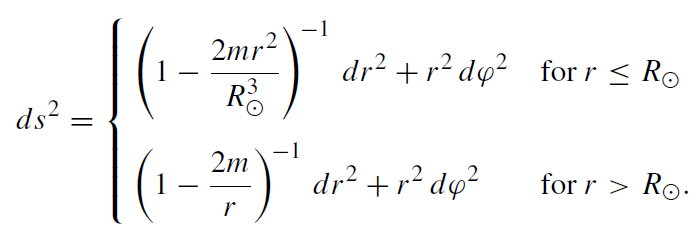 (1.2)
(1.2)
These metrics are equivalent to 2D metrics induced by the 3D Euclidean metric on a sphere or a hyperboloid, respectively. The 3D Euclidean metric is ds2 = dr2 + r 2 dφ2 + dz2. A surface rotationally symmetric around the z-axis is described by a parametrization z = z(r ). The metric induced on this surface is ds2 = [1+(dz/dr)2] dr2 +r 2 dφ2. By comparison with the previous metrics, we extract differential equations for z(r ) which can be easily solved. At r = Rּ, the surfaces are continuously joined (see figure 1.1).
Outside, we have the usual vacuum Schwarzschild geometry which was discussed extensively in the previous section. We may add a few remarks. Obviously, a circle (or sphere, respectively) around the origin has a circumference of 2πr, where r is the radial Schwarzschild coordinate. We also observe that the proper distance measured by a freely falling observer (who, in our picture, moves radially on the hyperboloid) is larger than the coordinate distance Δr . Inside the star we have the three-geometry of a sphere with radius ˆR. Far away from the star we find flat Euclidean geometry.
The structure of this three-geometry resembles the Newtonian case. Inside, we have a conformally flat space, where the Weyl (‘trace-free part of the curvature’) vanishes and the Ricci tensor is proportional to the mass-energy density. In the Newtonian case, the trace of the tidal matrix (the analogy to curvature) is proportional to the mass density, and, subsequently, its trace-free part vanishes. Outside, in vacuum, it is the other way around. There the trace parts are zero (Kaa = 0 and Ricαβ = 0 = R). The Newtonian tidal acceleration
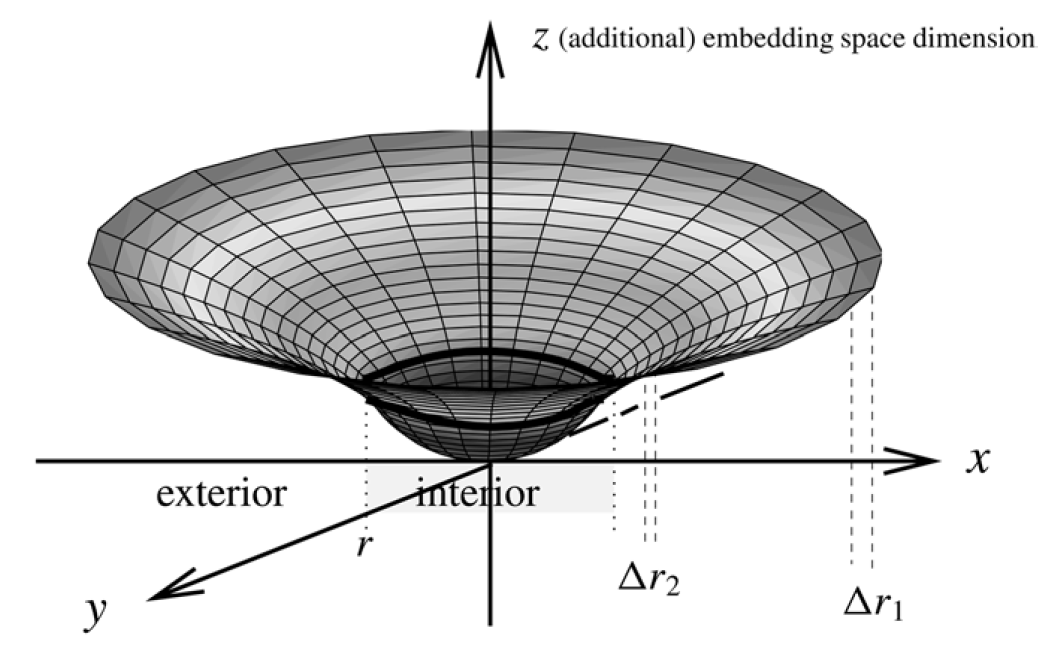
Figure 1.1. Geometry of Schwarzschild spacetime.
matrix is trace free and reads (in Cartesian coordinates, assume r = (0, 0, r )):
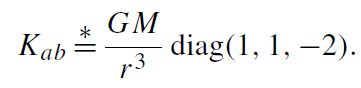 (1.3)
(1.3)
In Einstein's theory we have to use the equation for the geodesic in order to calculate the relative acceleration of two freely falling test particles. For the comoving observer, with uα = (c, 0, 0, 0) and in an orthonormal frame, we find
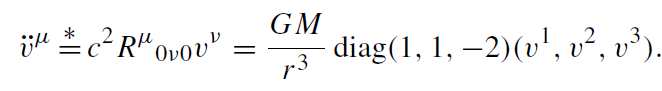 (1.4)
(1.4)
Thus, in a special frame, we have the same tidal accelerations as in the Newtonian case.
Accordingly, the gravitational field of a spherically symmetric body in Newton's 3D theory is very naturally embedded into Einstein's 4D theory.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


