


 تاريخ الرياضيات
تاريخ الرياضيات
 الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة
الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة 
 الرياضيات المتقطعة
الرياضيات المتقطعة
 الجبر
الجبر
 الهندسة
الهندسة 
 المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية
المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية 
 التحليل
التحليل
 علماء الرياضيات
علماء الرياضيات |
Read More
Date: 3-1-2017
Date: 10-1-2017
Date: 12-1-2017
|
The decimal number system is familiar to every reader and will be used to illustrate the meaning of the binary system. When we write the number 3814, each of the digits 3, 8, 1, and 4 conveys a meaning dependent on its position within the number: 3 refers to thousands, 8 to hundreds, 1 to tens, and 4 to units. Another way of conveying the same information is to write the number as a sum of multiples of powers of 10. Here we have
3814 = 3(103) + 8(102) + 1(101) + 4(100).
Having written 3814 in this way, we can easily observe the significance of 10 in our decimal system. The number 10 is referred to as the radix of the decimal system.
Any positive integer greater than 1 could serve as a radix as well as the integer 10. For instance, the number 194 written in radix 5 would read 1234, meaning that
194 = 1(53) +2 (52) + 3(51) + 4(50).
The same number in radix 7 would read 365, meaning 3(72) + 6(71) +5(70). If a radix larger than 10 were used, it would be necessary to create some new symbols, since in any system, an integer smaller than the radix should be represented by a single digit.
To make the ideas just introduced more precise, we will define a digit to be any single symbol used to represent a nonnegative integer. A number is defined to be a symbol consisting of a sequence of k + 1 digits, N = ak …..a2a1a0, where each ai is a digit. A number is related to the radix R of the number system by the equation
N = akRk+... + a2R 2 + a1R + a0.
To convert any number N from the decimal system to the system with radix R, the following method will serve.
1. Determine the highest power, k, of R which does not exceed N.
2. Divide N by Rk. The quotient, ak, is the first digit of N and the remainder, r1, is used in step 3.
3. (a) If r1 is larger than Rk-1, divide r1 by Rk-1 to obtain a quotient ak-1, the second digit of N, and a remainder r2 to be used in step 4.
(b) If r1 is smaller than Rk-1, the second digit of N is 0, and r1 is used in step 4.
4. Repeat step 3 with the result of (a) or (b) and continue until all powers of R less than k have been used.
EXAMPLE 1. Convert 97 to the number system with radix 3.
Solution. 34 equils 81 and is the highest power of 3 less than 97. 97 - 81 is 1 with remainder 16. The first digit of 97 in radix 3 is therefore 1. Now since 33 = 27 is larger than 16, the second digit is 0. Next, 16 is divided by 32 = 9 to give a quotient 1 and remainder 7. Thus the third digit is 1. Next, 7 is divided by 3 to give the quotient 2, the fourth digit, and remainder 1. Division by 30 = 1 gives a quotient 1, the last digit of our number. Thus we find that the decimal number 97 should be written as 10,121 in the number system with radix 3.
To change from a given radix to the decimal system, it is necessary only to expand according to the definition in terms of powers of the radix and evaluate the resulting sum as a number in decimal notation.
EXAMPLE 2. Find the decimal equivalent of 2312 in the system of radix 4.
Solution. 2312 in radix 4 means
2(43) + 3(42) +1(4) + 2 = 128 +48 + 4 = 2,
which is equal to 182 in decimal notation.
The radix 2 is of special interest since a number written in radix 2 contains only two digits, 0 and 1. It is easy to see how such a number can be represented by a sequence of switches, lights, relays, or other devices, each of which has two states corresponding to 0 and 1. The system using radix 2 is called the binary number system. The general discussion above will serve to define radix 2 but, for convenience, Table 6-1 is included to show the first sixteen numbers in both the decimal system and the binary system.
For conversion of an arbitrary number from the binary system to the decimal, or from the decimal to the binary, the methods above may be used.
TABLE 1-1
BINARY AND DECIMAL REPRESENTATIONS OF NUMBERS
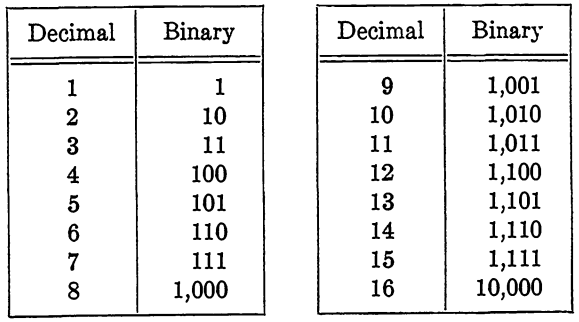
Fractions may also be introduced in the binary system by considering negative powers of 2 and separating the number by a period at the appropriate place exactly as is done in the decimal system. We will limit the discussion in this chapter to whole numbers for the sake of simplicity, but no great difficulty is added with the inclusion of fractions. As an illustration, 3/4 in decimal notation is 0.75, which means 7(10-1) + 5(10-2). In the binary system, 4 is written as 0.11, meaning 1(2-1) + 1(2-2).



|
|
|
|
دراسة يابانية لتقليل مخاطر أمراض المواليد منخفضي الوزن
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اكتشاف أكبر مرجان في العالم قبالة سواحل جزر سليمان
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
اتحاد كليات الطب الملكية البريطانية يشيد بالمستوى العلمي لطلبة جامعة العميد وبيئتها التعليمية
|
|
|