
Speed of Sound in Quantum Gases
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 33
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 33
 4-9-2016
4-9-2016
 1917
1917
Speed of Sound in Quantum Gases
The sound velocity u in a spin-1/2 Fermi gas is given at τ = 0 by

where ρ = mn, m is the mass of the gas particles, and n is the number density.
a) Show that

where μ is the chemical potential.
b) Calculate the sound velocity in the limit of zero temperature. Express your answer in terms of n, m.
c) Show that

in a Bose gas below the Bose–Einstein temperature.
SOLUTION
a) The Gibbs free energy G is a function of (P, τ), which do not depend on the number of particles; i.e.,
 (1)
(1)
where f(P, τ) is some function of (P, τ). On the other hand,
 (2)
(2)
Therefore, μ = G/N for a system consisting of identical particles, and we may write for μ:
 (3)
(3)
where s = S/N and v = V/N. From (3) we have

and we recover
 (4)
(4)
b) The number of quantum states in the interval between p and p + dp for a Fermi gas is
 (5)
(5)
where g = 2s + 1. At τ = 0, electrons fill all the states with momentum from 0 to pF, so the total number of electrons N is given by
 (6)
(6)
For s = 1/2, g = 2, and
 (7)
(7)
or
 (8)
(8)
The total energy of the gas
 (9)
(9)
Substituting pF from (8), we obtain
 (10)
(10)
Using the equation of state for a Fermi gas,

we have
 (11)
(11)
Now, using (11), we can calculate u2:
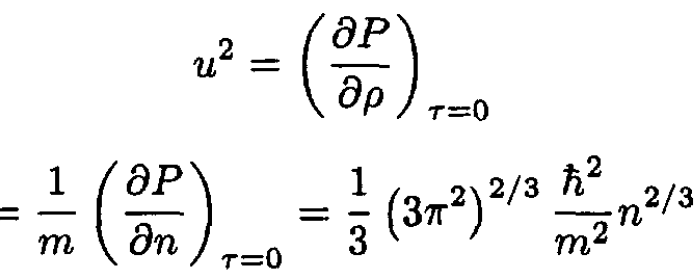 (12)
(12)
Alternatively, we can use the expression obtained in (a) and the fact that, at τ = 0, the chemical potential μ ≡ εF. From (8),
 (13)
(13)
and we again recover (12) in
 (14)
(14)
c) We can explicitly calculate the total energy of the Bose gas, which will be defined by the particles that are outside the condensate (since the condensed particles are in the ground state with ε = 0). At a temperature below the Bose–Einstein condensation τ < τ0, the particles outside the condensate (with ε > 0) are distributed according to a regular Bose distribution with μ = 0:
 (15)
(15)
The total number of particles outside the condensate is  therefore
therefore
 (16)
(16)
The energy of the Bose gas at τ < τ0 is
 (17)
(17)
The free energy F is

since G = μN and μ = 0. So the pressure
 (18)
(18)
So we see that the pressure does not depend on the volume and

at τ < τ0. We could have determined the result without the above calculations since μ = 0 at τ ≤ τ0; the particles which are inside the condensate (with ε = 0) have no momentum and do not contribute to pressure.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


