

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
3-8-2016
1927
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
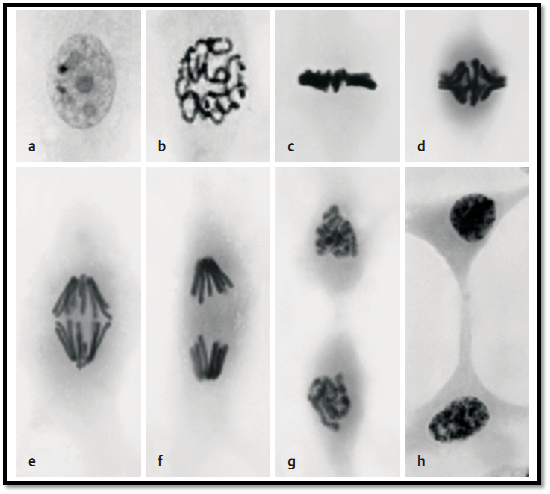
The most common type of nuclear cell division is mitosis. Mitosis yields two genetically identical daughter nuclei. It is followed by cell division ( cytokinesis). The inactive period between active periods of cell division is called interphase. Nuclear division and cell division are the high points of the cell cycle. This cycle is segmented into the phases G1, S, G2 and mitosis. Mitosis is complete d in six consecutive steps. The figure on the right presents different stages of mitosis. The dividing cells were Indian muntjac fibroblasts in cell culture ( Muntiacus muntjac ).
a) Interphase. Phase between divisions. The chromatin is dispersed or forms small aggregates. It is often possible to distinguish between highly con-dense d chromatin, called heterochromatin, and less densely packed chromatin, called euchromatin. One or two nucleoli are routinely present.
b) Prophase. Begin of mitosis. The chromatin condenses to form chromosomal threads, which b ecome increasingly thicker and shorter (coil stage, spirem). The nucleolus dissolves and the nuclear membrane falls apart.
The nuclear spindle forms and provides the apparatus for chromosome movement. The nuclear membrane dissolves in the following prometa-phase.
c) Metaphase. The chromosomes are arranged in the equatorial plane of the spindle, the metaphase plane. It now becomes apparent that there are two identical sister chromatids in each chromosome. Each chromatid has an area for the attachment to one of the spindle fibers, which extends to both spindle poles. This is the stage when karyotyping works best.
d-f) Anaphase. The two identical sister chromatids separate and move to the cell pole. Phase of the double (daughter) stars or diaster. In a later ana-phase stage, a cytokinetic actin ring forms in the position of the equatorial plane.
g) Telophase. Completion of the nuclear division. The chromatids combine and form a coil. A new nuclear membrane forms, the cytoplasm divides by contracting the cytokinetic actin ring (division ring) ( cytokinesis ). Anew cell wall is synthesized in the place of the cytokinetic actin ring.
h) Interphase.
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















