

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Dense Regular Connective Tissue-Tendon
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
الجزء والصفحة:
8-1-2017
6984
Dense Regular Connective Tissue-Tendon
The taut, dense regular connective tissue with parallel fibers is the prototype of tendons ( strand-like form ), aponeuroses ( flat, planar form) and ligaments. This figure shows part of a longitudinal section through a finger tendon. The structural components of tendons are strong, stress-absorbing collagen fibers that are commensurate with their mechanical tasks. The collagen fibers (stained red) assemble in a parallel arrangement ( primary collagen bundles). Relaxed fibers undulate slightly. Fibroblasts and their row of nuclei line up between fiber bundles. These cells are also called tendon cells ( tenocytes ). The tenocytes are in part captured in planar view and in part seen as profiles . The geometry of tendon cells adapts to the spatial conditions inside the tendon structure.
Stain: alum hematoxylin-eosin; magnification: × 240
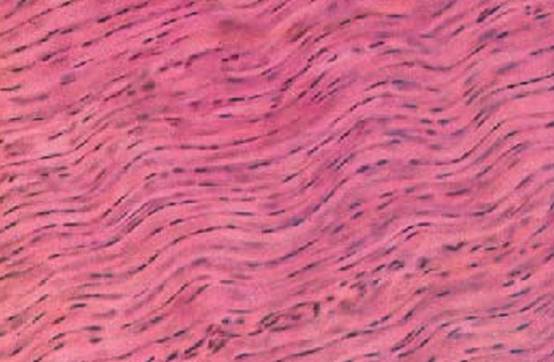
Dense Regular Connective Tissue—Tendon
Cross-section through a tendon. Each of the fiber bundles in the tendon are encased by loose, fibrous, vascularized connective tissue ( peritendineum internum) 1 , which subdivides the tendon into secondary bundles. The tendon cells ( winged cells ) extend thin, wing-like cytoplasmic processes in all directions. The cell processes adhere closely to the collagen fibers. The light crevices are technical artifacts (shrinkage due to fixation). The tendon surface is covered by the peritendineum externum (epitendineum), which is a braided web of connective tissue. The epitendineum itself is covered at the outside with loose connective tissue called peritendineum .
1 Peritendineum internum
Stain: alum hematoxylin-eosin; magnification: × 130
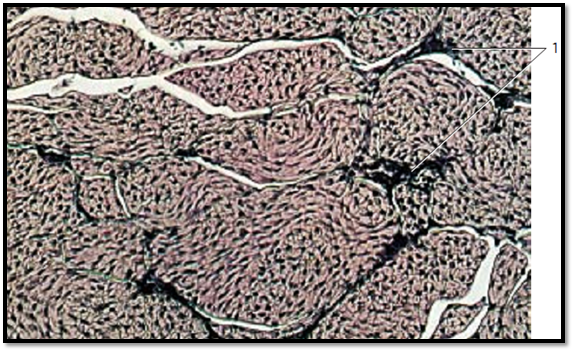
Dense Regular Connective Tissue—Tendon
Cross-section through the tendon ( primary collagen bundle) of the long finger flexor from a mouse. Several bundles of differently sized collagen fibrils 1 are cut. In light microscopy, every bundle of fibrils corresponds to a fiber. Between the bundles of fibrils are tendon cells 2 —i.e., modified fibrocytes ( tenocytes ). Their slender cytoplasmic processes ex-tend wing-like into the narrow spaces between fibril bundles (“winged cells”) 3 . These cytoplasmic processes interconnect with each other. Tendon cells contain plenty of granular endoplasmic reticulum (rER) 4 , mitochondria and lysosomes 5 .
1 Fibril bundles
2 Nuclei of tendon cells
3 Cytoplasmic processes of tendon cells
4 Cytoplasm of tendon cells with rER
5 Lysosomes
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 8300
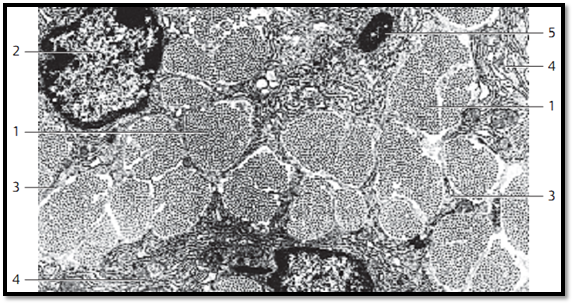
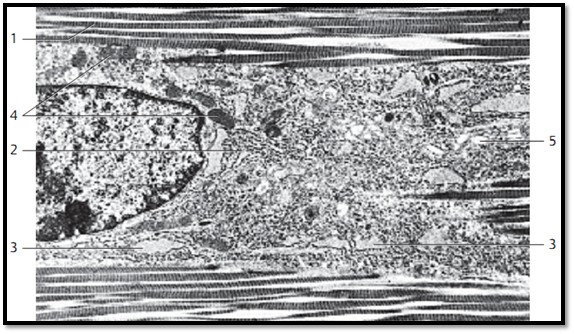
Dense Regular Connective Tissue—Tendon
This cross-section through the tendon of the human long finger flexor out-lines the wide range for the diameters of collagen fibrils 1 . There is also a sec-tion through part of a tendon cell ( fibrocyte, tenocyte ) with its nucleus 2 and long, extended, slender processes (wings) 3 , which adhere snugly to the fibrils. Tendon cells usually have long, extended nuclei and little cytoplasm. Note the narrow perinuclear band of cytoplasm 4 .
1 Collagen fibrils, cut vertical to their axis
2 Nucleus of a tendon cell
3 Cytoplasmic processes (wing)
4 Small cytoplasmic band (seam)
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 20000
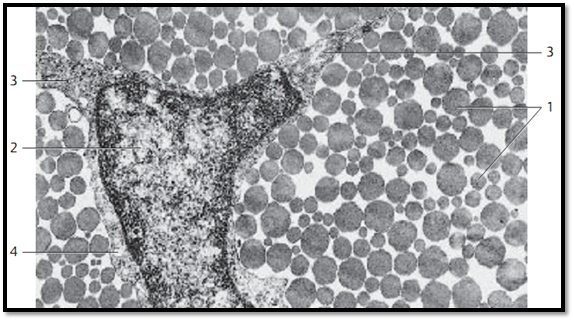
Dense Regular Connective Tissue—Tendon
Longitudinal section through the tendon (primary collagen bundle)from the long finger flexor of a mouse. The collagen fibrils 1 are cut lengthwise and show the typical cross-striation . The section shows the perikaryon of a tendon cell ( fibrocyte, tenocyte ) between fibril bundles. The cytoplasm contains rER lamella 2 and in some sections, small rER cisternae 3 .It also contains mitochondria 4 and Golgi complexes 5 . Aponeuroses are planar tendons. Their structures resemble that of collagen ligaments.
1 Collagen fibrils
2 Granular endoplasmic reticulum, rER
3 Rough ER cisternae
4 Mitochondria
5 Golgi apparatus
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 6500
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















