
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Components of velocity, acceleration, and force
المؤلف:
Richard Feynman, Robert Leighton and Matthew Sands
المصدر:
The Feynman Lectures on Physics
الجزء والصفحة:
Volume I, Chapter 9
2024-02-05
1624
In Eq. (9.4) we have resolved the velocity into components by telling how fast the object is moving in the x–direction, the y–direction, and the z–direction.

The velocity is completely specified, both as to magnitude and direction, if we give the numerical values of its three rectangular components:

On the other hand, the speed of the object is
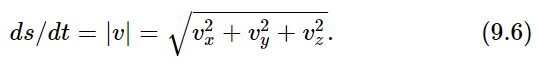

Fig. 9–2. A change in velocity in which both the magnitude and direction change.
Next, suppose that, because of the action of a force, the velocity changes to some other direction and a different magnitude, as shown in Fig. 9–2. We can analyze this apparently complex situation rather simply if we evaluate the changes in the x–, y–, and z–components of velocity. The change in the component of the velocity in the x–direction in a time Δt is Δvx=axΔt, where ax is what we call the x–component of the acceleration. Similarly, we see that Δvy=ayΔt and Δvz=azΔt. In these terms, we see that Newton’s Second Law, in saying that the force is in the same direction as the acceleration, is really three laws, in the sense that the component of the force in the x–, y–, or z–direction is equal to the mass times the rate of change of the corresponding component of velocity:

Just as the velocity and acceleration have been resolved into components by projecting a line segment representing the quantity, and its direction onto three coordinate axes, so, in the same way, a force in a given direction is represented by certain components in the x–, y–, and z–directions:

where F is the magnitude of the force and (x,F) represents the angle between the x–axis and the direction of F, etc.
Newton’s Second Law is given in complete form in Eq. (9.7). If we know the forces on an object and resolve them into x–, y–, and z–components, then we can find the motion of the object from these equations. Let us consider a simple example. Suppose there are no forces in the y– and z–directions, the only force being in the x–direction, say vertically. Equation (9.7) tells us that there would be changes in the velocity in the vertical direction, but no changes in the horizontal direction. This was demonstrated with a special apparatus in Chapter 7 (see Fig. 7–3). A falling body moves horizontally without any change in horizontal motion, while it moves vertically the same way as it would move if the horizontal motion were zero. In other words, motions in the x–, y–, and z–directions are independent if the forces are not connected.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















