


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 24-6-2022
Date: 2023-08-18
Date: 2023-11-15
|
Received pronunciation (RP)
RP is the socially prestigious but regionally unmarked pronunciation used predominantly by British newsreaders: while British English accents are regional, an RP speaker could come from anywhere within the UK, although RP’s features are predominantly southern English in origin. For all the reverence accorded to this pronunciation, RP is an accent like any other and is subject to change: the speech of BBC newsreaders who used RP in 1940s and 1950s newsreels sounds very different from that of today’s RP users. Where the latter would have the a vowel close to Cardinal 4 in hat [hat], for example, the former would have insisted on a vowel raised to somewhere between Cardinals 3 and 4 [æ].
The secondary cardinal vowels 9–16 simply reverse the lip-rounding value of their primary counterparts; thus Cardinal 9, [y], which corresponds to the vowel in French tu or German süss, is simply Cardinal 1, [i], with firmly rounded lips. Likewise Cardinals 10 and 11, the vowels of standard French feu 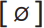 and fleuve [œ] respectively, are the rounded equivalents of 2 and 3. Cardinal 12,
and fleuve [œ] respectively, are the rounded equivalents of 2 and 3. Cardinal 12,  , the rounded equivalent of [a], is rare cross-linguistically, but Cardinal 13,
, the rounded equivalent of [a], is rare cross-linguistically, but Cardinal 13, 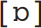 , is used in RP body or cot (most US English varieties have an unrounded vowel here). Cardinal 14 [V] is the conservative RP pronunciation of the cup vowel (most southern English speakers have a more fronted variant). Cardinals 15
, is used in RP body or cot (most US English varieties have an unrounded vowel here). Cardinal 14 [V] is the conservative RP pronunciation of the cup vowel (most southern English speakers have a more fronted variant). Cardinals 15 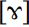 and 16
and 16  are less familiar to speakers of the major western European languages, but both occur in Scots Gaelic and Thai, and Cardinal 16 is an important vowel in Japanese.
are less familiar to speakers of the major western European languages, but both occur in Scots Gaelic and Thai, and Cardinal 16 is an important vowel in Japanese.
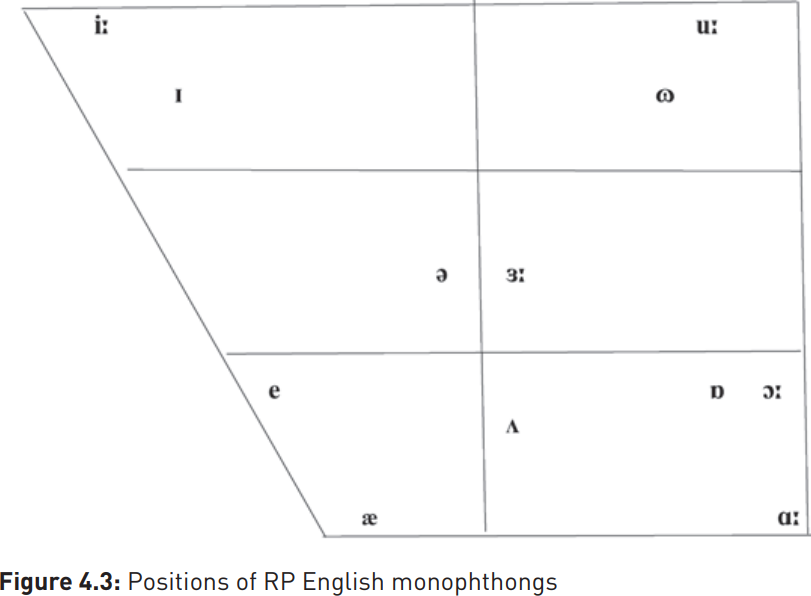

Helpful though the cardinal vowels are as reference points, they do not correspond closely with the vowel positions of English, which are shown in the diagrams below. For the RP vowels in push 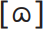 (the older symbol
(the older symbol 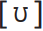 is also used) and kick [I], for example, the tongue is retracted to a more central position from [u] and [i] respectively, and requires less muscular effort (for this reason these two vowels are sometimes called lax vowels). Confusingly, some of the phonemic symbols for RP vowels no longer correspond to their modern pronunciation. Textbooks still refer, for example, to /æ/ and
is also used) and kick [I], for example, the tongue is retracted to a more central position from [u] and [i] respectively, and requires less muscular effort (for this reason these two vowels are sometimes called lax vowels). Confusingly, some of the phonemic symbols for RP vowels no longer correspond to their modern pronunciation. Textbooks still refer, for example, to /æ/ and  in spite of the fact that, for most RP speakers, these vowels have moved to [a] and
in spite of the fact that, for most RP speakers, these vowels have moved to [a] and  respectively. The modern positions of RP monophthongs can be seen in Figure 4.3.
respectively. The modern positions of RP monophthongs can be seen in Figure 4.3.
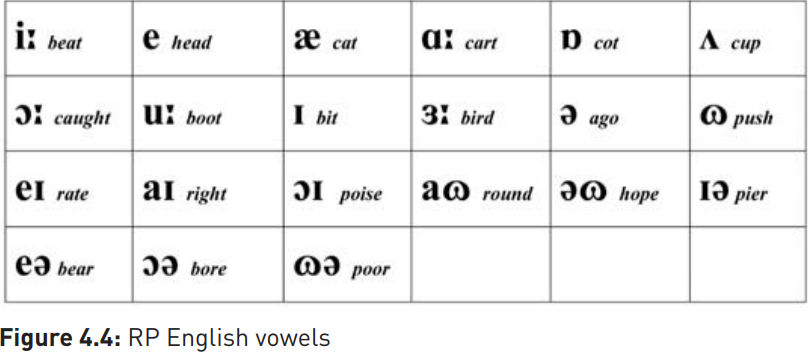
RP has one long central vowel, [3:], the vowel in bird, which may bear stress, and another, schwa, 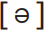 , which cannot. Generally, vowels produced at the centre of the vocal tract require least articulatory effort. When asked a question and needing a bit of thinking time, many speakers naturally start their reply with ‘Er…’, the sound produced with the tongue in the central rest position. Although schwa has no letter of its own in English orthography (Bulgarian uses the Cyrillic character ъ, Turkish has ı), it is a very important sound in English and in many other languages. For most British English speakers it is the underlined vowel in each of the following words: potato, reader, banana, support, phonetic. In both English and French it can, in some cases, can be deleted altogether, so that in rapid speech, for example, sport and support can be homophonous.
, which cannot. Generally, vowels produced at the centre of the vocal tract require least articulatory effort. When asked a question and needing a bit of thinking time, many speakers naturally start their reply with ‘Er…’, the sound produced with the tongue in the central rest position. Although schwa has no letter of its own in English orthography (Bulgarian uses the Cyrillic character ъ, Turkish has ı), it is a very important sound in English and in many other languages. For most British English speakers it is the underlined vowel in each of the following words: potato, reader, banana, support, phonetic. In both English and French it can, in some cases, can be deleted altogether, so that in rapid speech, for example, sport and support can be homophonous.
|
|
|
|
للعاملين في الليل.. حيلة صحية تجنبكم خطر هذا النوع من العمل
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
"ناسا" تحتفي برائد الفضاء السوفياتي يوري غاغارين
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بمناسبة مرور 40 يومًا على رحيله الهيأة العليا لإحياء التراث تعقد ندوة ثقافية لاستذكار العلامة المحقق السيد محمد رضا الجلالي
|
|
|