
Storage capacity
 المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
 الجزء والصفحة:
121
الجزء والصفحة:
121
 17-4-2021
17-4-2021
 1890
1890
Storage capacity
Recall that the unit of energy is the watt hour (Wh) or the kilowatt hour (kWh). Any electrochemical cell or battery has a certain amount of electrical energy that can be gotten rom it, and this can be specified in watt hours or kilowatt hours. More often though it’s given in ampere hours (Ah).
A battery with a rating of 2 Ah can provide 2 A for an hour, or 1 A for 2 hours. Or it can provide 100 mA for 20 hours. Within reason, the product of the current in amperes, and the use time in hours, can be as much as, but not more than 2. The limitations are the shelf life at one extreme, and the maximum safe current at the other. Shelf life is the length of time the battery will last if it is sitting on a shelf without being used; this might be years. The maximum safe current is represented by the lowest load resistance (heaviest load) that the battery can work into before its voltage drops because of its own internal resistance. A battery is never used with loads that are too heavy, because it can’t supply the necessary current anyway, and it might “boil”, burst, or blow up.
Small cells have storage capacity of a few milliampere hours (mAh) up to 100 or 200 mAh. Medium-sized cells might supply 500 mAh or 1 Ah. Large automotive or truck batteries can provide upwards of 50 Ah. The energy capacity in watt hours is the ampere- hour capacity times the battery voltage.
When an ideal cell or battery is used, it delivers a fairly constant current for awhile, and then the current starts to fall off (Fig. 1). Some types of cells and batteries approach this ideal behavior, called a flat discharge curve, and others have current that declines gradually, almost right from the start. When the current that a battery can provide has tailed off to about half of its initial value, the cell or battery is said to be “weak.” At this time, it should be replaced. If it’s allowed to run all the way out, until the current actually goes to zero, the cell or battery is “dead.” Some rechargeable cells and batteries, especially the nickel-cadmium type, should never be used until the current goes down to zero, because this can ruin them.
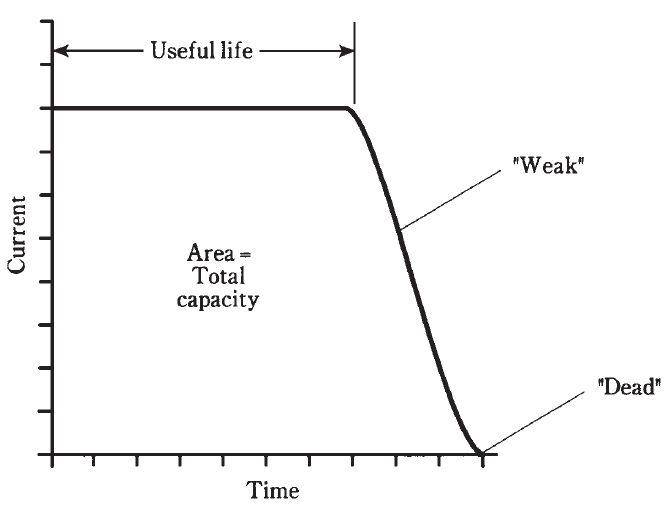
Fig. 1: A flat discharge curve. This is considered ideal.
The area under the curve in Fig. 1 is the total capacity of the cell or battery in ampere hours. This area is always pretty much the same for any particular type and size of cell or battery, regardless of the amount of current drawn while it’s in use.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


