
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Molecules
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
الجزء والصفحة:
10
29-3-2021
2071
Molecules
When atoms of elements join together to form a compound, the resulting particles are molecules. Figure 1 is an example of a molecule of water, consisting of three atoms put together.
The natural form of an element is also known as its molecule. Oxygen tends to occur in pairs most of the time in the earth’s atmosphere. Thus, an oxygen molecule is sometimes denoted by the symbol O2. The “O” represents oxygen, and the subscript 2 indicates that there are two atoms per molecule. The water molecule is symbolized H2O, because there are two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen in each molecule.
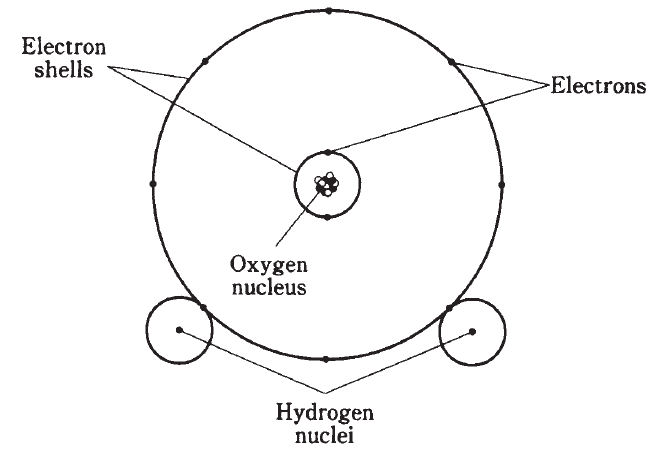
Figure 1: Simplified diagram of a water molecule.
Sometimes oxygen atoms are by themselves; then we denote the molecule simply as O. Sometimes there are three atoms of oxygen grouped together. This is the gas called ozone, that has received much attention lately in environmental news. It is written O3.
All matter, whether it is solid, liquid, or gas, is made of molecules. These particles are always moving. The speed with which they move depends on the temperature. The hotter the temperature, the more rapidly the molecules move around. In a solid, the molecules are interlocked in a sort of rigid pattern, although they vibrate continuously (Fig. 2A). In a liquid, they slither and slide around (Fig. 2B). In a gas, they are literally whizzing all over the place, bumping into each other and into solids and liquids adjacent to the gas (Fig. 2C).

Figure 2: At A, simplified rendition of molecules in a solid; at B, in a liquid; at C, in a gas. The molecules don’t shrink in the gas. They are shown smaller because of the much larger spaces between them.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















