

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Insect Resistance
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
12-12-2020
1456
Insect Resistance
Chemical control of insect pests is both expensive and environmentally unfriendly. Worldwide expenditure on insecticides and the value of crop losses from insect predations have been estimated in Table .
Transgenic cotton, maize and potato crops are being grown commercially which express Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) toxins to confer resistance to chewing insects. On sporulation, B. thuringiensis synthesizes S-endotoxin crystalline proteins encoded by Cry genes. On ingestion by an insect, prototoxins are cleaved in the alkaline midgut to the active toxin. This binds to specific receptors in the gut epithelial cells, which results in the formation of pores and eventually to the death of the insect. Some advantages of Bt toxins include:
(i) Specificity – each Cry protein is active against only one or a few insect species.
(ii) Diversity – many different Cry proteins have been identified.
(iii) Reduced or no detrimental effects identified on non-target insects or natural enemies of insects.
(iv) Very low mammalian toxicity.
(v) Easily degradable.
The production of transgenic Bt expressing insect resistant crops has been a high commercial priority, but effective production of Bt toxins required re-engineering of Cry genes for plant codon usage and removal of cryptic signals (e.g. splice sites, polyadenylation signals). These changes permit efficient expression of Bt toxins in plants, with both fulllength and truncated versions of Cry genes used successfully for insect
Table . Worldwide costs of insecticides and losses caused by insects
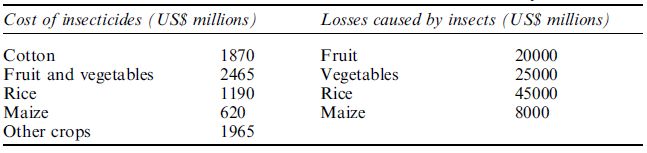
resistance. Now, more than 40 different genes containing insect resistance have been incorporated into transgenic crops with several commercialised in different countries such as the USA and Australia. Given the usefulness of Bt toxins for insect control, various management strategies must be adopted to delay development of insect resistance to Bt. These include:
(i) setting aside areas of non-Bt cotton as refuges to reduce the selection pressure towards insect resistance;
(ii) deploying different insect resistance genes (e.g. protease inhibitors);
(iii) using multiple Bt toxins which target different receptors;
(iv) use of spray inducible promoters to control expression of Bt genes;
(v) use of tissue-specific promoters such that insects can feed
unharmed on economically less important parts of the plant. It is mandatory to set aside non-transgenic refuges when growing Bt cotton, maize and potatoes. Even with additional costs associated with this and other agronomic management practices, the growth of Bt cotton gives higher returns to farmers, environmental benefits (50–80% less chemicals used, spraying reduced from 10–12 per year to 4–5 per year) and less occupational exposure of farm workers to sprays. There are other approaches under development for transgenic insect resistance,including those based on: protease inhibitors, a amylase inhibitors, lectins, chitinases, cholesterol oxidase, cloned insect viruses, tryptophan decarboxylase, anti-chymotrypsin, anti-elastase, bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor and spleen inhibitor.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















