Ion exchange HPLC
Ion exchange HPLC is based on the partition of ions between a polar liquid phase and a stationary phase with ion exchange sites. The ion exchange sites are typically immobilized in small beads of resin that are formed by a cross-linked polymer. Bonded phase columns in which the ion exchanger is bonded to small particles of silica also are available. Cations are separated on cation exchange resins which contain negatively charged functional groups such as SO3- and –COO-. Anions are separated on anion exchange resins which contain positively charged functional groups such as CH2N+ (CH3)3, a quaternary ammonium ion. Separation is based on ions partitioning into the ion exchange phase to varying degrees. The selectivity of a resin for an ion is determined primarily by the charge on the ion and its hydrated radius. Resin affinity increases with increasing charge density.
Instrumentation
The apparatus consists of a container of the mobile phase, a pump capable of pressures up to 4000 psi or greater, a valve for injecting the sample (usually 10 to 500 μL volumes), the column (sometimes thermostatted), a detector, electronics associated with the detector, and a recorder. A schematic of the HPLC instrument can be seen in Figure 1.1. This instrument in this lab used a C18 column.
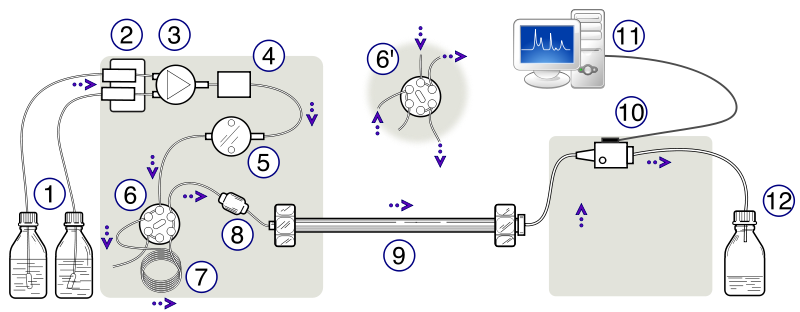
Figure 1.1: Schematic Diagram of a High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph. (1) Solvent reservoirs, (2) Solvent degasser, (3) Gradient valve, (4) Mixing vessel for delivery of the mobile phase, (5) High-pressure pump, (6) Switching valve in "inject position", (6') Switching valve in "load position", (7) Sample injection loop, (8) Pre-column or guard column, (9) Analytical column, (10) Detector (i.e. IR, UV), (11) Data acquisition, (12) Waste or fraction collector. Created by Yassne Mrabet.
UV-visible absorbance is the most commonly used mode of detection. Such detectors enable the component (or effluent) from the column to flow through an 8 to 10 μL spectrophotometric cell for detection of compounds at a particular wavelength (often in the ultraviolet, < 400nm, where many organic molecules absorb). Electrochemical and fluorescence detectors often are used to achieve lower detection limits. The other commonly used detector is based on a measurement of the differential refractive index.


