

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
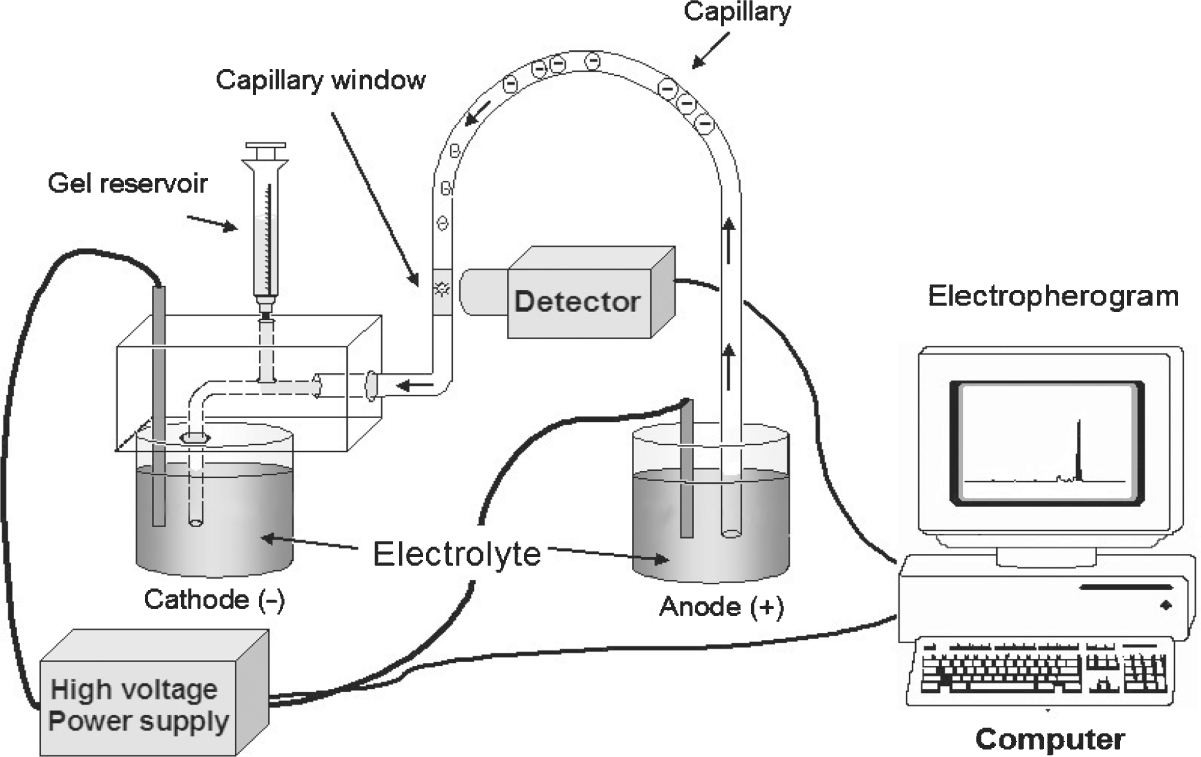
Capillary Electrophoresis: Instrumental Setup
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
15-2-2020
4079
Capillary Electrophoresis: Instrumental Setup
A typical capillary electrophoresis system consists of a high-voltage power supply, a sample introduction system, a capillary tube, a detector and an output device. Some instruments include a temperature control device to ensure reproducible results. This is because the separation of the sample depends on the electrophoretic mobility and the viscosity of the solutions decreases as the column temperature rises.3 Each side of the high voltage power supply is connected to an electrode. These electrodes help to induce an electric field to initiate the migration of the sample from the anode to the cathode through the capillary tube. The capillary is made of fused silica and is sometimes coated with polyimide.3 Each side of the capillary tube is dipped in a vial containing the electrode and an electrolytic solution, or aqueous buffer. Before the sample is introduced to the column, the capillary must be flushed with the desired buffer solution. There is usually a small window near the cathodic end of the capillary which allows UV-VIS light to pass through the analyte and measure the absorbance. A photomultiplier tube is also connected at the cathodic end of the capillary, which enables the construction of a mass spectrum, providing information about the mass to charge ratio of the ionic species.
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















