

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Argon-ion Lasers
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
28-2-2020
2498
Argon-ion Lasers
Another commonly used gas laser is the argon-ion laser. In these lasers, as in the He-Ne the lasing transition type is atomic. But instead of a neutral atom, here the lasing is the result of the de-excitations of the ion. It takes more energy to ionize an atom than to excite it. By the same token, more energy can be obtained from the de-excitation of the ion. So, doubly (Ar++) and singly ionized (Ar+) argon atoms can radiate shorter wavelength light than could the neutral argon atom, Ar. Because of this, argon-ion lasers can produce uv light with a wavelength as short as 334 nm. In addition, these lasers can produce much more power than He-Ne lasers. Argon-ion lasers typically range in output power from one to as much as 20 W. At the higher power levels their output is multi-mode, i.e. contains several distinct wavelengths. Some of these wavelengths are:
- 334 nm, UV
- 351 nm, UV
- 364 nm, UV
- 458 nm, violet
- 477 nm , violet
- 488 nm, (strong) blue
- 497 nm, blue-green
- 514 nm, (strongest) green
Because of these two reasons, high power and multicolor output, argon-ion is one of the most commonly used lasers in laser light shows, as well as in a variety of applications.
The make-up of a typical argon-ion laser is very similar to a He-Ne's, but with a few slight differences. First, these lasers are much larger in size. A typical Ar++ laser tube is about one meter long, as compared to just 20 cm for that of a He-Ne. Second, the optical cavity of these lasers is built external to the tube. This is partly because of the high power operation of the laser and partly because such external arrangement allows for the use of optional wavelength selection optics within the optical cavity. A prism or a diffraction grating located just before the high reflecting mirror selects only one of the lasing transitions for amplification within the cavity; other wavelengths are deflected out of the resonant cavity. In this way these ion lasers can operate in a so called single mode.

With this arrangement the two mirrors holders on opposite sides of the laser tube are typically attached together with an invar rod for thermal stabilization (Invar is a steel alloy that contains nickel). Its most valued property is that it expands and contracts very little when its temperature changes. As a result, when the laser's temperature changes as it heats up due to the large electric current within the electromagnetic pump discharge, the optical path length, and therefore the modal character of the laser output, remains relatively unchanged. Finally, because of their high power argon-ion lasers require active cooling. This is most commonly accomplished by circulating water, either directly from tap or from commercially produced chillers, in closed coils that surround the plasma (a gas of charged ions) tube and parts of the electric power supply. Some of the lower powered argon-ion lasers are just air cooled using a fan, which makes them less cumbersome to use.
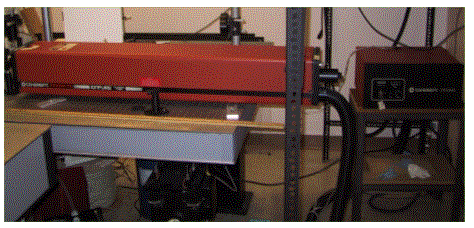
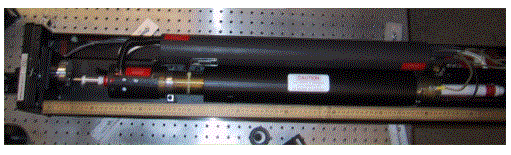
The above two photographs show a 5 W argon-ion laser. Notice the one-meter long laser tube, the large ballast, and the umbilical cord that connects to the laser power supply. This cord contains not only the power line that supplies the laser with the electric power to generate the plasma, but also the water lines that circulate water to cool the laser.
Another type of ion laser, the krypton laser, operates very much the same as the argon-ion laser. To take advantage of all the colors available in both argon and krypton lasers, manufacturers make argon-krypton ion lasers by using a suitable mixture of these two gases. The mixed gas lasers are very useful for entertainment applications because, in addition to many colors, they can also produce a "white" beam. (Why is the word "white" in quotations?)
 الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
الاكثر قراءة في التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















