

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
Homology Calculations-The Homology Groups of an Octohedron
المؤلف:
David R. Wilkins
المصدر:
Algebraic Topology
الجزء والصفحة:
73-77
28-6-2017
1939
Let K be the simplicial complex consisting of the triangular faces, edges and vertices of an octohedron in R3 with vertices P1, P2, P3, P4, P5 and P6, where
P1 = (0, 0, 1), P2 = (1, 0, 0), P3 = (0, 1, 0),
P4 = (−1, 0, 0), P5 = (0, −1, 0), P6 = (0, 0, −1)
This octohedron consists of the four triangular faces P1P2P3, P1P3P4, P1P4P5 and P1P5P2 of the pyramid whose base is the square P2P3P4P5 and whose apex is P1, together with the four triangular faces P6P2P3, P6P3P4, P6P4P5 and P6P5P2 of the pyramid whose base is P2P3P4P5 and whose apex is P6.
A typical 2-chain c2 of K is a linear combination, with integer coefficients, of eight oriented 2-simplices that represent the triangular faces of the octohedron. Thus we can write

(The orientation on each of these triangles has been chosen such that the vertices of the triangle are listed in anticlockwise order when viewed from a point close to the centre of triangle that lies outside the octohedron.) Similarly a typical 1-chain c1 of K is a linear combination, with integer coefficients, of twelve 1-simplices that represent the edges of the octohedron.
Thus we can write

where rk ∈ Z for k = 1, 2, . . . , 6.
We now calculate the boundary of a 2-chain. It follows from the definition of the boundary homomorphism ∂2 that

Now C3(K) = 0, and thus B2(K) = 0 (where 0 here denotes the zero group), since the complex K has no 3-simplices. Therefore H2(K) ∼= Z2(K) ∼= Z.
Next we calculate the boundary of a 1-chain. It follows from the definition of the boundary homomorphism ∂1 that

On examining the structure of these equations, we see that, when c1 is a 1- cycle, it is possible to eliminate five of the integer quantities mj , expressing
them in terms of the remaining quantities. For example, we can eliminate m4, m6, m7, m8 and m12, expressing these quantities in terms of m1, m2, m3, m5, m9 m10 and m11 by means of the equations
m4 = −m1 − m2 − m3,
m6 = m2 − m10 + m5,
m7 = m2 + m3 − m10 − m11 + m5,
m8 = −m1 + m9 + m5,
m12 = −m9 − m10 − m11
It follows that
Z2(K) = {m1z1 + m2z2 + m3z3 + m5z5 + m9z9 + m10z10 + m11z11},
where
z1 = ρ1 − ρ4 − ρ8 = −∂2σ4,
z2 = ρ2 − ρ4 + ρ6 + ρ7 = ∂2(σ2 + σ3),
z3 = ρ3 − ρ4 + ρ7 = ∂2σ3,
z5 = ρ5 + ρ6 + ρ7 + ρ8 = ∂2(σ1 + σ2 + σ3 + σ4),
z9 = ρ8 + ρ9 − ρ12 = −∂2σ8,
z10 = −ρ6 − ρ7 + ρ10 − ρ12 = ∂2(σ6 + σ7),
z11 = ρ11 − ρ7 − ρ12 = ∂2σ7.
From these equations, we see that the generators z1, z2, z3, z5, z9, z10 and z11 of the group Z1(K) of 1-cycles all belong to the group B1(K) of 1-boundaries.
It follows that Z1(K) = B1(K), and therefore H1(K) = 0.
In order to determine H0(K) it suffices to note that the 0-chains
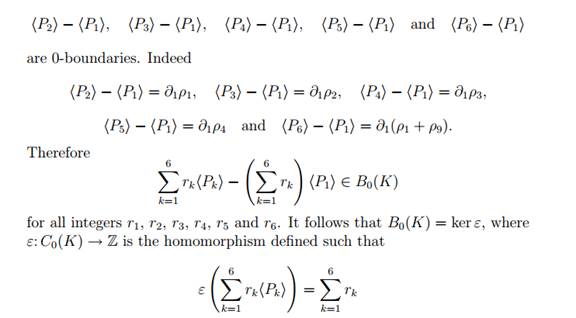
for all integers rk (k = 1, 2, . . . , 6). Now Z0(K) = C0(K) since the homomorphism ∂0: C0(K) → C−1(K) is the zero homomorphism mapping C0(K) to the zero group. It follows that
H0(K) = C0(K)/B0(K) = C0(K)/ ker ε ≅Z.
(Here we are using the result that the image of a homomorphism is isomorphic to the quotient of the domain of the homomorphism by the kernel of the homomorphism.)
We have thus shown that
H2(K)≅Z, H1(K) = 0, H0(K) ≅ Z.
One can show that Z1(K) = B1(K) by employing an alternative approach to that used above. An element z of Z1(K) is of the form z =∑12j=1 mjρj, where
m1 + m2 + m3 + m4 = 0, m1 − m5 + m8 − m9 = 0,
m2 + m5 − m6 − m10 = 0, m3 + m6 − m7 − m11 = 0,
m4 + m7 − m8 − m12 = 0 and m9 + m10 + m11 + m12 = 0.
The 1-cycle z belongs to the group B1(K) if and only if there exists some 2-chain c2 such that z = ∂2c2. It follows that z ∈ B1(K) if and only if there exist integers n1, n2, . . . , n8 such that
m1 = n1 − n4, m2 = n2 − n1, m3 = n3 − n2, m4 = n4 − n3,
m5 = n1 − n5, m6 = n2 − n6, m7 = n3 − n7, m8 = n4 − n8,
m9 = n5 − n8, m10 = n6 − n5, m11 = n7 − n6, m12 = n8 − n7.
The integers n1, n2, . . . , n8 solving the above equations are not uniquely determined, since, given one collection of integers n1, n2, . . . , n8 satisfying these equations, another solution can be obtained by adding some fixed integer to each of n1, n2, . . . , n8. It follows from this that if there exists some collection n1, n2, . . . , n8 of integers that solves the above equations, then there exists a solution which satisfies the extra condition n1 = 0. We then find that
n1 = 0, n2 = m2, n3 = m2 + m3, n4 = −m1,
n5 = −m5, n6 = m2 − m6, n7 = m2 + m3 − m7, n8 = −m1 − m8.
On substituting n1, n2, . . . , n8 into the relevant equations, and making use of the constraints on the values of m1, m2, . . . , m12, we find that we do indeed have a solution to the equations that express the integers mj in terms of the integers ni. It follows that every 1-cycle of K is a 1-boundary. Thus Z1(K) = B1(K), and therefore H1(K) = 0.
 الاكثر قراءة في التبلوجيا
الاكثر قراءة في التبلوجيا
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















