
Trigonometric functions of any angle
 المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
 المصدر:
www.almerja.com
المصدر:
www.almerja.com
 الجزء والصفحة:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
 13-2-2017
13-2-2017
 2428
2428
Trigonometric functions of any angle
Unit circle. Counting of angles in a unit circle.
Negative and positive angles. Quarters of a unit circle.
Sine and cosine lines. Sine. Cosine. Signs of sine and
cosine in different quarters of a unit circle. Tangent
and cotangent lines. Tangent. Cotangent. Signs of
tangent and cotangent in different quarters of a unit
circle. Secant and cosecant.
To build all trigonometry, laws of which would be valid for any angles ( not only for acute angles, but also for obtuse, positive and negative angles), it is necessary to consider so called a unit circle, that is a circle with a radius, equal to 1 ( Fig.3 ).
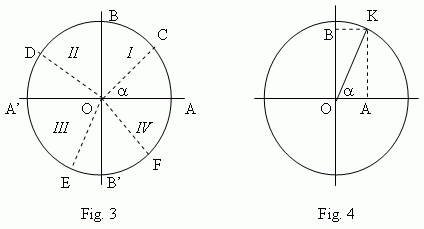
Let draw two diameters: a horizontal AA’ and a vertical BB’. We count angles off a point A (starting point). Negative angles are counted in a clockwise, positive in an opposite direction. A movable radius OC forms angle α with an immovable radius OA. It can be placed in the 1-st quarter ( COA ), in the 2-nd quarter ( DOA ), in the 3-rd quarter ( EOA ) or in the 4-th quarter ( FOA ). Considering OA and OB as positive directions and OA’ and OB’ as negative ones, we determine trigonometric functions of angles as follows.
A sine line of an angle  ( Fig.4 ) is a vertical diameter of a unit circle, a cosine line of an angle α - a horizontal diameter of a unit circle. A sine of an angle α ( Fig.4 ) is the segment OB of a sine line, that is a projection of a movable radius OK to a sine line; acosine of an angle
( Fig.4 ) is a vertical diameter of a unit circle, a cosine line of an angle α - a horizontal diameter of a unit circle. A sine of an angle α ( Fig.4 ) is the segment OB of a sine line, that is a projection of a movable radius OK to a sine line; acosine of an angle  - the segment OA of a cosine line, that is a projection of a movable radius OK to a cosine line.
- the segment OA of a cosine line, that is a projection of a movable radius OK to a cosine line.
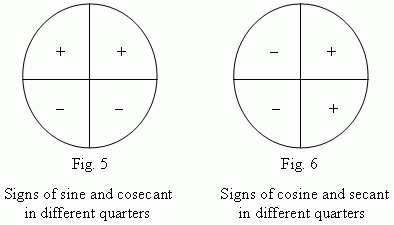
Signs of sine and cosine in different quarters of a unit circle are shown on Fig.5 and Fig.6.
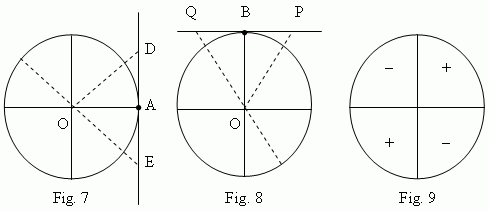
A tangent line ( Fig.7 ) is a tangent, drawn to a unit circle through the point A of a horizontal diameter.
A cotangent line ( Fig.8 ) is a tangent, drawn to a unit circle through the point B of a vertical diameter.
A tangent is a segment of a tangent line between the tangency point A and an intersection point ( D, E, etc., Fig.7 ) of a tangent line and a radius line.
A cotangent is a segment of a cotangent line between the tangency point B and an intersection point ( P, Q, etc., Fig.8 ) of a cotangent line and a radius line.
Signs of tangent and cotangent in different quarters of a unit circle see on Fig.9.
Secant and cosecant are determined as reciprocal values of cosine and sine correspondingly.
 الاكثر قراءة في المثلثات
الاكثر قراءة في المثلثات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


