
Radian and degree measures of angles
 المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
المؤلف:
المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتيه
 المصدر:
www.almerja.com
المصدر:
www.almerja.com
 الجزء والصفحة:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
 9-2-2017
9-2-2017
 2435
2435
Radian and degree measures of angles
Degree and radian measures of angles.
Relation of a circle radius and a circumference
length. Table of degree and radian measures
for some most used angles.
A degree measure. Here a unit of measurement is a degree (its designation is ° or deg ) – a turn of a ray by the 1 / 360 part of the one complete revolution. So, the complete revolution of a ray is equal to 360 deg. One degree is divided into 60 minutes (a designation is ‘ or min); one minute – correspondingly into 60 seconds (a designation is “ or sec).
A radian measure. As we know from plane geometry ( see the point "A length of arc" of the paragraph "Geometric locus. Circle and circumference"), a length of an arc l , a radius r and a corresponding central angle α are tied by the relation:
α = l / r .
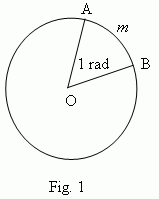
This formula is a base for definition of a radian measure of angles. So, if l = r , then α = 1, and we say, that an angle α is equal to1 radian, that is designed as α = 1 rad. Thus, we have the following definition of a radian measure unit:
A radian is a central angle, for which lengths of its arc and radius are equal ( AmB = AO, Fig.1 ). So, a radian measure of any angle is a ratio of a length of an arc drawn by an arbitrary radius and concluded between sides of this angle to the arc radius.
Following this formula, a length of a circumference C and its radius r can be expressed as:
2 α = C / r .
So, a round angle, equal to 360° in a degree measure, is simultaneously 2α in a radian measure. Hence, we receive a value of one radian:
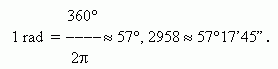
Inversely,
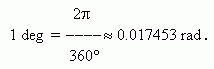
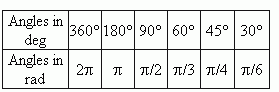
It is useful to remember the following comparative table of degree and radian measure for some angles, we often deal with:
 الاكثر قراءة في المثلثات
الاكثر قراءة في المثلثات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


