
Palatine Tonsil
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 23-1-2017
23-1-2017
 3148
3148
Palatine Tonsil
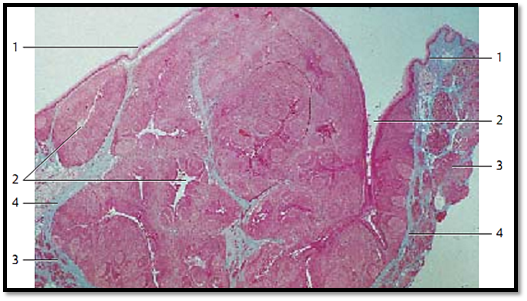
The palatine tonsils are covered by the mucous membranes of the oral cavity 1 (multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium). The tonsils show about 15–20 deep, of ten branched crypts 2 ( fossulae tonsillares ). The crypts extend deep into the lymphoreticular tissue of the tonsil. A wall of lymphoreticular tissue with secondary follicles surrounds each crypt. A connective tissue capsule separates the palatine tonsil from the surrounding and the Killian muscle. In the figure, at the right and left, the muscles of the palatopharyngeal arch 3 are cut.
1 Epithelium of the oral cavity
2 Tonsillar crypts
3 Killian muscle, musculature of the palatopharyngeal arch
4 Connective tissue capsule
Stain: azan; magnification: × 10
Palatine Tonsil
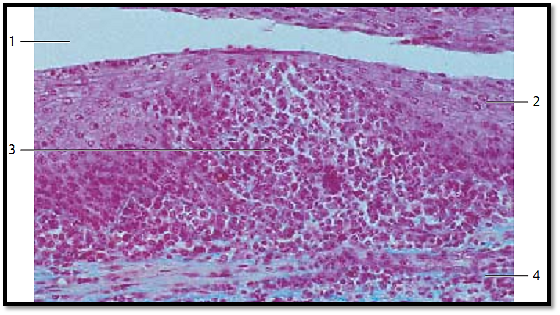
Longitudinal section of a crypt from the palatine tonsil with the adjacent layer of lymphoreticular tissue, which is part of the lamina propria of the mucous membrane. The multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium 1 at the mouth of the crypt and the tonsillar surface shows hardly any lymphocytes. Only in the depth of the crypt 2 is the squamous epithelium infiltrated by lymphocytes. Consequently, the epithelium there is more loosely organized and the structural integrity of the epithelium diminished. The germinal centers 3 display an incomplete layer that looks like a cap 4 with the top directed toward the crypt. This layer consists of small lymphocytes (B-lymphocytes). The T-cell region is locate d in the interfollicular zone 5 .
1 Multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium from the oral mucous membranes
2 Crypt
3 Germinal center
4 Follicle cap (B-lymphocyte cap) 5 Inter follicular areas
Stain: alum hematoxylin-eosin; magnification: × 12

Palatine Tonsil
Longitudinal section of the tonsillar crypt 1 . In the center of the figure, the structure of the multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium 2 of the oral mucous membranes is completely obliterate d by lymphocytes 3 .It now has the structure of a sponge. The underlying lymphoreticular tissue 4 follows without clear demarcation. The multilayered squamous epithelium to the right and left is for the most part intact. Only a few small, heavier stained lymphocytes reside in this part of the layer. The epithelium of the adjacent crypt wall (top of the figure) appears unchanged. Inflammation (tonsillitis) may cause increased scaling of epithelial cells. This, and the increased presence of leukocytes and microorganisms of the oral cavity, can lead to tonsillar plugs (detritus plugs, tonsillar abscess). Occasionally, these will calcify and form tonsillar stones.
1 Tonsillar crypt
2 Multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium
3 Lymphocyte immigration and leukocytic diapedesis
4 Lymphoreticular tissue
Stain: azan; magnification: × 200
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


