
Free Connective Tissue-Mast Cells
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 11-1-2017
11-1-2017
 2003
2003
Free Connective Tissue-Mast Cells
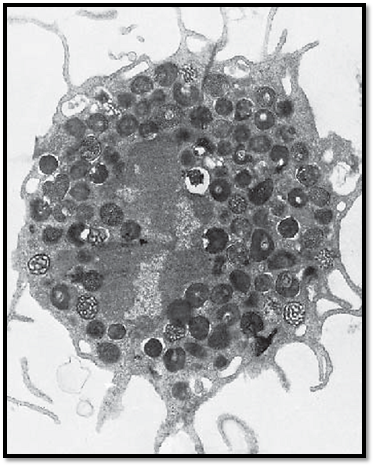
This mast cell was isolated from lung tissue. It shows long cell processes, some of which are branched. The cells establish contact with each other via these processes. This creates the image of a three-dimensional, more or less elaborate, peripheral network . In the cell center is an arcuate, notched nucleus with heterochromatin at its periphery. The cytoplasm displays a dense, finely granular matrix. Apart from this specific granulation, there are few organelles. The cell-specific, membrane-enclosed granules have diameters of about 0.5–1.5 μm. They are amorphous, both in form and structure. There are two distinct mast cell types—mucosa mast cells in the connective tissue of mucous membranes and tissue mast cells in the connective tissue of the skin.
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 13600
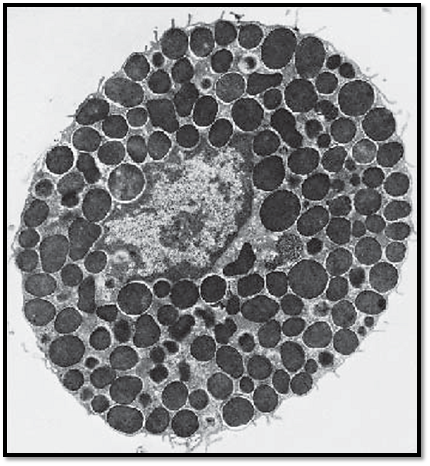
This transmission electron microscopic image displays the typical ultrastructure of a tissue mast cell from a rat. On the surface are sporadic short plasma membrane processes. The central nucleus is relatively small and shows peripheral heterochromatin. The nucleus is dente d in several places because of the close vicinity to cell-specific granules. The cytoplasm contains the specific round or oval granules, which have diameters of about 0.5–1.5 μm. The granules are always enclose d by a membrane and separate d from other granules by cytoplasmic septa, which contain crista-type mitochondria, Golgi complexes and, sporadically, filaments. The matrix of each granule is homogeneous and electron-dense. Based on their sulfate d glycosaminoglycan content, mast cells show a meta-chromatic reaction—i.e., their granules appear between blue-violet and re d after staining with a blue alkaline thiazine dye. The granules contain heparin and the biogenic amine histamine. Heparin inhibits blood clotting and is a potent anticoagulant. Histamine causes the arteries and arterioles in connective tissue to dilate. There are two different types of mast cells—the tissue mast cells in the connective tissue of the skin and the mucosa mast cells in the connective tissue of mucous membranes.
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 11400
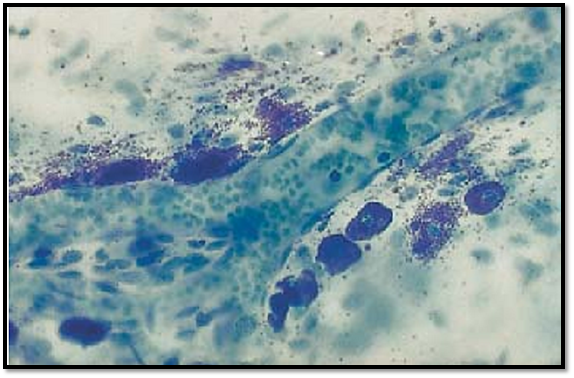
Several mast cells are lined up along a dividing arteriole. They are about 10–12 μm long and contain blue-violet (metachromatic) granules . The cell nuclei in the center are often obscure d because granules cover them. The release of mast cell granules into the extracellular space ( exocytosis) is triggered either by nonspecific stimuli or by antigen-antibody reactions. In this preparation, there are also many metachromatic granules present in the free connective tissue space. This whole-mount preparation (not a section) is from the peritoneal lining of a rat diaphragm. The arteriole contains blood cells.
Stain: toluidine blue; magnification: × 400
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


