
Free Connective Tissue Cells-Plasma Cells
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 11-1-2017
11-1-2017
 2067
2067
Free Connective Tissue Cells-Plasma Cells
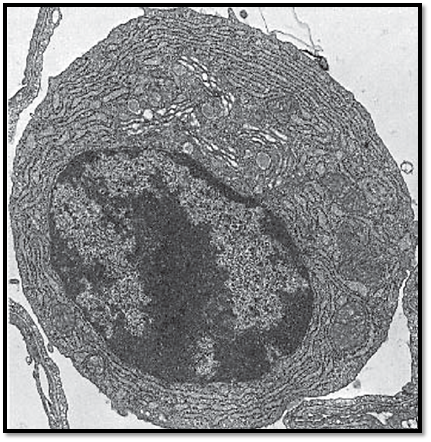
Plasma cells are most frequently found in the cellular connective tissue of various organs (lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, lung, lamina propria of the intestinal mucosa). They are sporadically found in connective tissue every-where in the body, except in blood. They are abundant in areas with chronic inflammation. Plasma cells are round or polyhedral with rounded or oval nuclei, usually in an eccentric location. The chromatin structure is characteristic of these cells. Starting at the nucleolus, it extends to the inner nuclear membrane in a star-like fashion. Chromatin accumulates at the inner nuclear membrane. This creates the wheel-spoke nucleus, as seen in light microscopy. Plasma cells are remarkably rich in intracellular granular membrane systems ( ergastoplasm ), which account for the basophilia. The mem-branes of the rough (granular) endoplasmic reticulum (rER) organize in a pattern and form cisternae in some locations. Rough ER membranes are absent from the Golgi region in the cell center. Crista-type mitochondria are present in the cytoplasm as well. Plasma cells are the final stage in the B-lymphocyte series. They are local (fixed) cells and do not divide; their lifespan is 10–30 days. They synthesize antibodies (proteins), and their function therefore serves the humoral immune response. Antibodies are release d (by extrusion ) without the formation of secretor y granules. Plasma cell from a lung (cat).
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 17000
Free Connective Tissue Cells—Plasma Cells
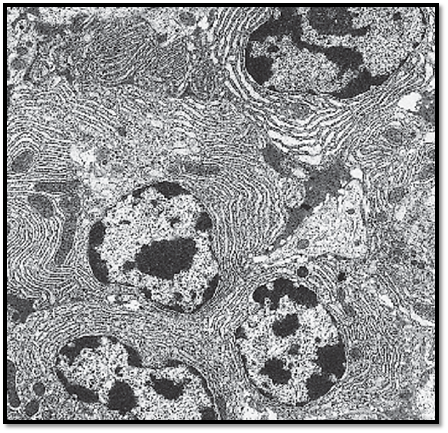
Plasma cells from the loosely organized connective tissue from the orbital gland of a sparrow. The cells are close together and form a small group. Plasma cells, the final cells in the B-lymphocyte series, are large, either oval or round and usually have round nuclei with dense coarse heterochromatin. Their characteristic is the abundance of granular (rough) endoplasmic reticulum (rER) as a location for immunoglobulin synthesis. It explains the conspicuous basophilia in light microscopy . In the plasma cell in the top right part of the figure, the rER cisternae are distended. All cells contain mitochondria of different sizes.
Electron microscopy; magnification: × 9000
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


