
Cornea
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel, W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 4-1-2017
4-1-2017
 2326
2326
Cornea
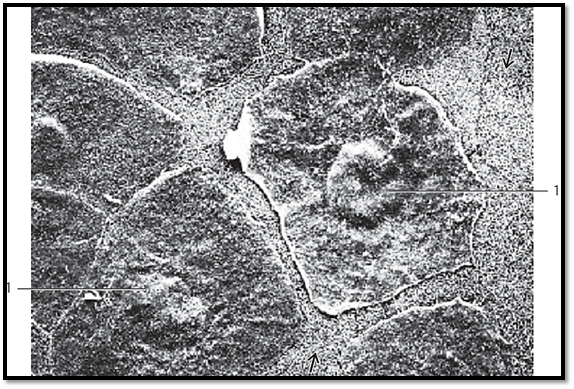
View of the surface of the corneal epithelium (surface cells, superficial cells). The polygonal cells are flattened and about 5 μm thick , with diameters up to 50 μm. Their nuclei protrude slightly 1 . The surface cells are sloughed off continuously and replace d. The large cell in the center of the figure is about to detach. The cells of the next lower layer contain fine, dense surface plicae , which serve the intercellular attachment. The cornea consists of five layers:
1 Epithelium
2 Lamina limitans anterior (Bowman’s membrane)
3 Stroma
4 Lamina limitans posterior (Descemet’s membrane)
5 Endothelium
Scanning electron microscopy; magnification: × 2000
Cornea
This vertical section through the cornea provides a clear image of the layered structure. The outer covering consists of five or six layers of nonkeratinizing cells (multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium) 1. It is about 70 μm high and is supported by a basal membrane. The limiting lamina ( Bowman’s membrane ) 2 follows as a relatively wide layer. The thick corneal stroma (substantia propria corneae ) 3 features 20 0–250 densely stacked lamellae about 2 μm thick , with interleaved parallel oriented collagen fibrils. Fibrocytes (keratinocytes ) with cytoplasmic processes (“branched fibrocytes) are found between collagen fibrils. The corneal f ibrocytes appear spindle-shape d in vertical sections. The thinner posterior limiting lamella ( Descemet’s membrane ) separates the corneal stroma from the about 5 μm thick posterior single-layered corneal epithelium (corneal endothelium).
1 Anterior corneal epithelium
2 Anterior limiting lamina, Bowman’s membrane
3 Corneal stroma, substantia propria corneae with fibrocytes (keratinocytes)
4 Posterior corneal epithelium (corneal endothelium)
Stain: alum hematoxylin-eosin; magnification: × 50

Cornea
Multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium of the cornea. There are surface cells 1 , intermediary cells 2 and basal cells 3 . Compare with Fig. below.
1 Sur face cells
2 Intermediary cells
3 Basal cells
4 Anterior limiting lamina, Bowman’s membrane
5 Corneal stroma
6 Keratinocyte
Stain: hematoxylin-eosin; magnification: × 500
Cornea
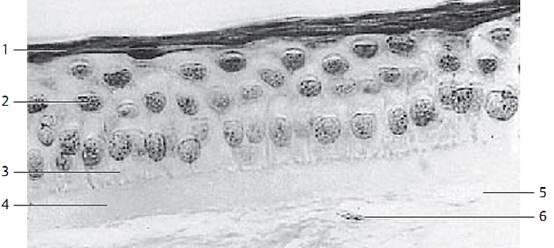
This vertical section of the cornea shows the corneal epithelium , Bowman’s membrane and the corneal stroma. Note the different shapes of the basal cells 3 and compare them with those in Fig. above. An intermediary cell of ten spans over two basal cells like an umbrella. The two uppermost layers consist of flattened, about 5 μm thick and up to 50 μm long flat surface cells 1. The anterior limiting lamina (Bowman’s membrane ) 4 lies under the epithelium. The lower part of the figure shows the corneal stroma 5 with long spindle-shape d f ibrocytes (keratinocytes ).
1 Sur face cells
2 Intermediary cells
3 Basal cells
4 Bowman’s membrane
5 Stroma corneae
Semi-thin section; stain: methylene blue-azure II; magnification: × 80

References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


