
Acceleration and Average Acceleration
 المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
المؤلف:
Professor John W. Norbury
 المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
المصدر:
ELEMENTARY MECHANICS & THERMODYNAMICS
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 49
الجزء والصفحة:
p 49
 12-12-2016
12-12-2016
 2808
2808
Acceleration and Average Acceleration
Again we follow the definitions made for 1-dimension. In 3-dimensions, the average acceleration is defined as
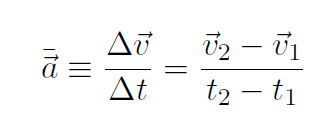
and acceleration (instantaneous acceleration) is defined as

Constant Acceleration Equations In 1-dimension, our basic definitions were
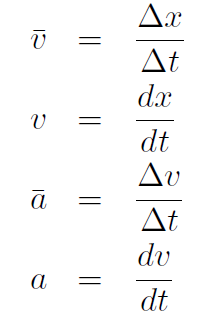
We found that if the acceleration is constant, then from these equations we can prove that
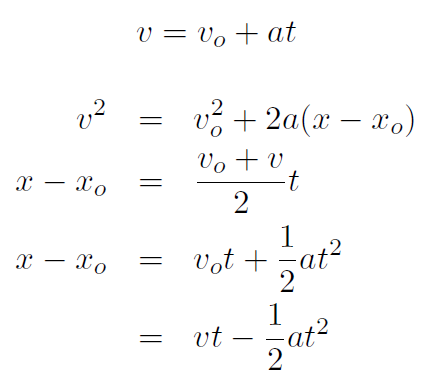
which are known as the 5 constant acceleration equations. In 3-dimensions we had
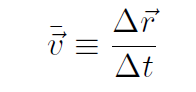
or
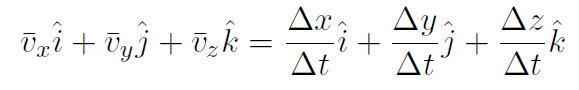
or
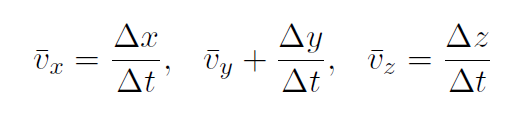
These 3 equations are the meaning of the first vector equation 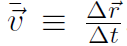 .
.
Similarly
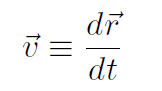
or
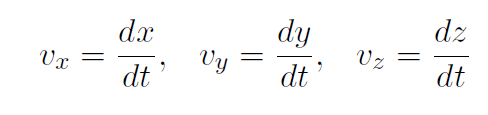
Similarly
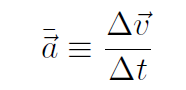
or
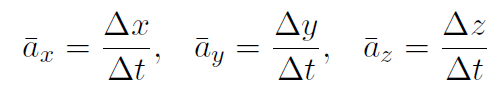
and
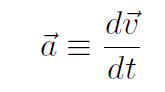
or

So we see that in 3-dimensions the equations are the same as in 1-dimension except that we have 3 sets of them; one for each dimension. Thus if the 3-dimensional acceleration vector 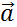 is now constant, then ax, ay and az must all be constant. Thus we will have 3 sets of constant acceleration equations, namely
is now constant, then ax, ay and az must all be constant. Thus we will have 3 sets of constant acceleration equations, namely
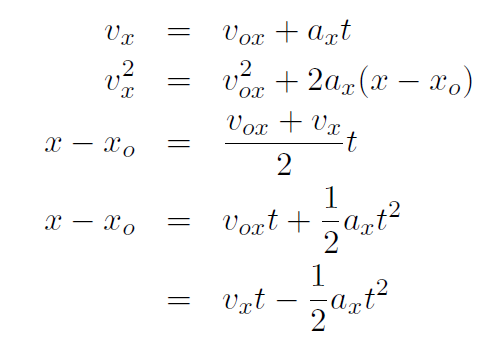
and

and
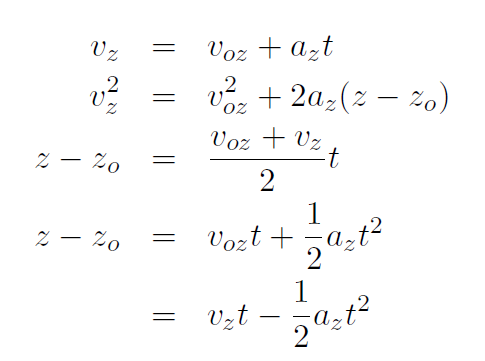
These 3 sets of constant acceleration equations are easy to remember. They are the same as the old ones in 1-dimension except now they have subscripts for x, y, z.
 الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
الاكثر قراءة في الميكانيك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


