
Multiple Genes For One Character
 المؤلف:
AN INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOLOGY-1998
المؤلف:
AN INTRODUCTION TO PLANT BIOLOGY-1998
 المصدر:
JAMES D. MAUSETH
المصدر:
JAMES D. MAUSETH
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 19-10-2016
19-10-2016
 2225
2225
Multiple Genes For One Character
Individual phenotypic traits are the result of complex metabolic processes involving numerous enzymes; therefore, many separate genes may affect any single trait. The gene R was described as affecting flower color by producing an enzyme that synthesized a red pigment.
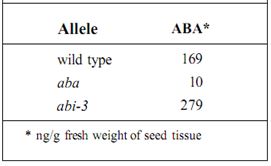
But that enzyme requires the proper substrate, which is present only if it is synthesized by a different enzyme controlled by a distinct gene. If this gene is present as an ineffective allele, there will be no substrate and thus no pigment, regardless of whether the first flower color gene is present as allele R or allele r. In Arabidopsis thaliana, abscisic acid AEA) causes developing seeds to become dormant at maturity. In several mutants (Table), mature embryos continue to grow as if germinating and do not enter dormancy. One mutant, aba, is unable to produce enough ABA. A second mutant, abi-3, produces plenty of ASA but does not respond to it—perhaps its ABA receptor is the affected protein. Although aba and abi-3 involve different genes, they both result in the same phenotype. They are multiple genes for one trait even though they are not part of one metabolic pathway.
Table : Multiple genes for one character
Most synthetic pathways involve at least four or five intermediates, and their four or five genes all affect the same trait. Having multiple genes for each trait is referred to as epistasis. Some intermediates may be produced by several pathways, each with its own enzymes; a mutation in one is not necessarily particularly severe, because the alternate pathway may increase its activity and produce sufficient amounts of the intermediate. If His happens, the mutation is masked and is not reflected in the phenotype, even if it is present in the homozygous condition. Conversely, when an intermediate is part of several metabolic pathways and is produced by only one enzyme, a mutation in that enzyme's gene affects all the pathways and alters several different traits. Multiple phenotype effects of one mutation are called pleiotropic effects. For example, any mutation that affects the protein potion of phytochrome affects all developmental processes controlled by phytochrome, and mutations that alter the level of pyruvate affect the citric acid cycle, amino acid synthesis, and C4 metabolism.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم النبات
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم النبات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


