
Thermal Expansion and Heat Capacity
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 45
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 45
 6-9-2016
6-9-2016
 1738
1738
Thermal Expansion and Heat Capacity
a) Find the temperature dependence of the thermal expansion coefficient if the interaction between atoms is described by a potential
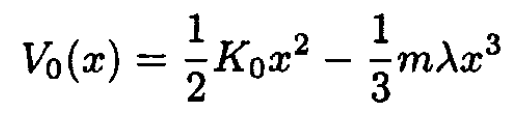
where λ is a small parameter.
b) Derive the anharmonic corrections to the Dulong–Petit law for a potential
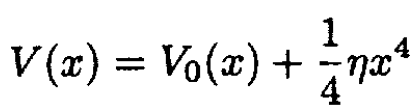
where η is a small parameter.
SOLUTION
a) First solution: We can calculate the average displacement of an oscillator:
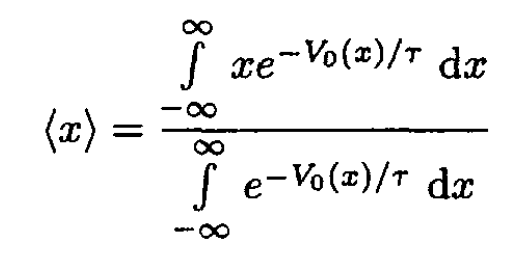 (1)
(1)
Since the anharmonic term is small, mλx3/3 << τ, we can expand the exponent in the integral:
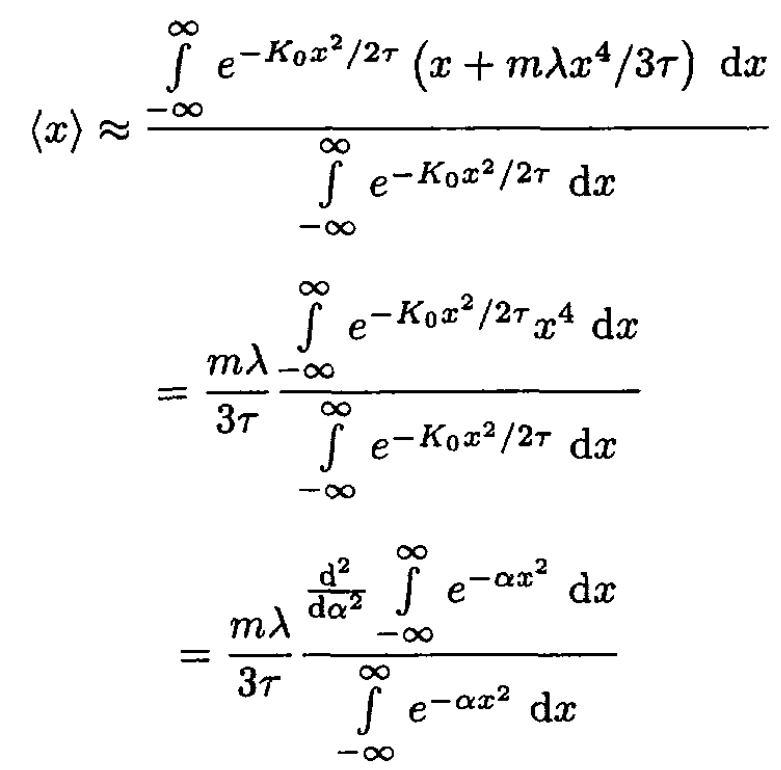 (2)
(2)
where we set α ≡ K0/2τ. So,
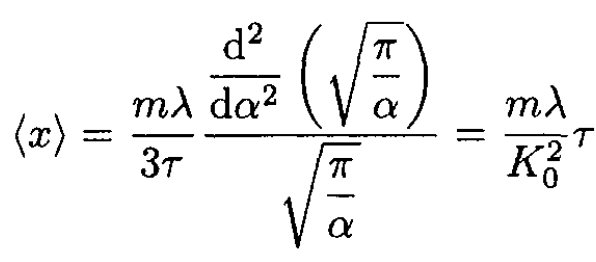 (3)
(3)
Note that, in this approximation, the next term in the potential would not have introduced any additional shift (only antisymmetric terms do).
would not have introduced any additional shift (only antisymmetric terms do).
Second solution: We can solve the equation of motion for the nonlinear harmonic oscillator corresponding to the potential V0(x):
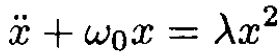 (4)
(4)
where 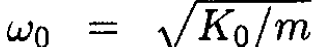 is the principal frequency. The solution gives
is the principal frequency. The solution gives
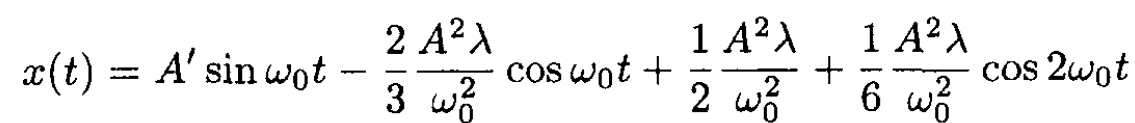 (5)
(5)
where A' is defined from the initial conditions and A is the amplitude of oscillations of the linear equation. The average ⟨x⟩ over a period T = 2π/ω0 is
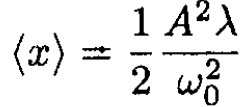 (6)
(6)
We need to calculate the thermodynamic average of ⟨x⟩:
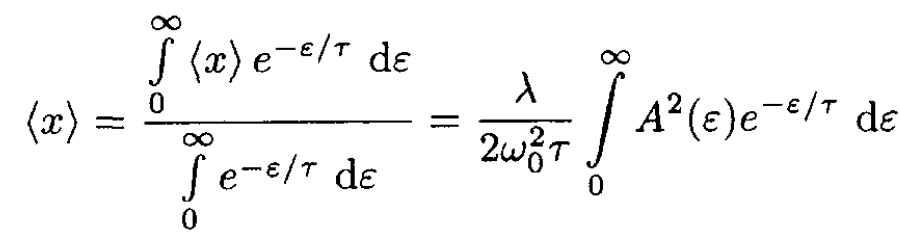 (7)
(7)
Substituting A2(ε) =2ε/K0, we obtain
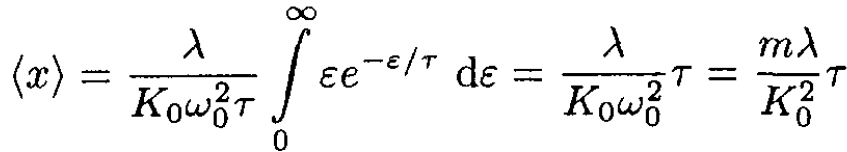 (8)
(8)
the same as before.
b) The partition function of a single oscillator associated with this potential energy is
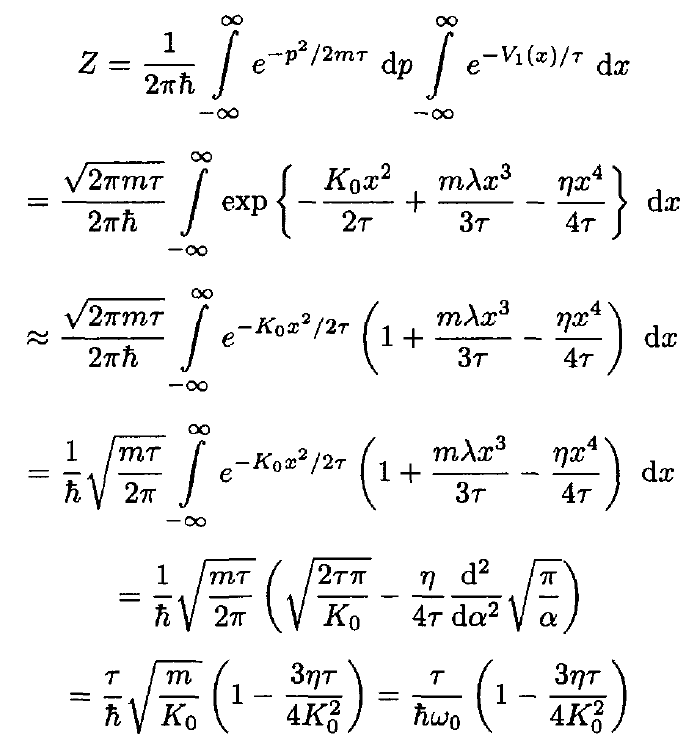 (9)
(9)
So, the free energy F per oscillator is given by
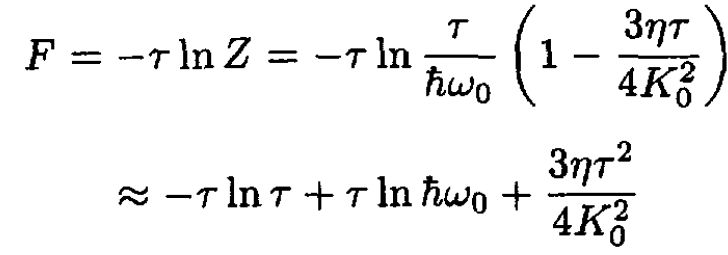 (10)
(10)
where we approximated ln (1 – x) ≈ - x. The energy per oscillator may be found from
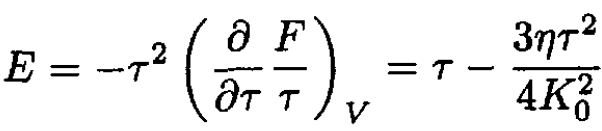 (11)
(11)
The heat capacity is then
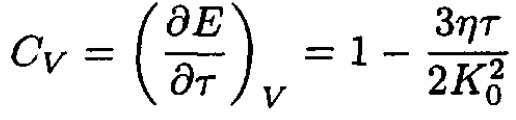 (12)
(12)
The anharmonic correction to the heat capacity is negative.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


