
Cell Nucleus
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 3-8-2016
3-8-2016
 3238
3238
Cell Nucleus
The nucleus is the center for the genetically determine d information in every eukaryotic cell. The nucleus also serves as a command or logistics center for the regulation of cell functions. There is a correlation between the geometry of the nucleus and the cell dimensions, which of fers important diagnostic clues. The nucleus is usually round in polygonal and isoprismatic (cuboid) cells and ellipsoid in Pseudostratified columnar cells; it has the form of a spindle in smooth muscle cells and is flattened in flat epithelial cells. In granulocytes, the nucleus has several segments. The fibrocytes in this figure is from subcutaneous connective tissue. Its elongate d, irregularly lob e d nucleus shows indentations and deep dells. The structural components of a nucleus are the nuclear membrane, the nuclear lamina, the nucleoplasm, and the chromosomes with the chromatin and the nucleolus. The chromatin is finely granular (euchromatin ), but more dense near the inner nuclear membrane ( heterochromatin). The small electron-dense patches are heterochromatin structures as well. The DNA is packaged in a much denser form in heterochromatin than in euchromatin, and heterochromatin therefore appears more heavily stained in light microscopy preparations. A nucleolus is not shown here. The cytoplasm of the fibrocytes contains mitochondria 1 , osmophilic secretory granules 2 , vesicles, free ribosomes and fragments of the rough (granular) endoplasmic reticulum membranes. Collagen fibrils are cut longitudinally or across their axis 3 .

Detail section showing two secretory cells from the mucous membranes of the tuba uterina (oviduct). Their long, oval nuclei show multiple indentations of different depths. Therefore, the nucleus appears to be composed of tongues and irregular lobes in this preparation. The cytoplasm extends into the deep nuclear indentations. The distribution of the finely granular chromatin ( euchromatin ) is relatively even. Only at the inner nuclear membrane is the chromatin condensed in a fine osmophilic line. The cytoplasm in the immediate vicinity of the nucleus contains cisternae from granular endoplasmic reticulum 1 , secretory granules 2 and sporadically, small mitochondria.

Rectangular nucleus in an orbital gland cell from the water agama (lizard). The nucleus contains two strikingly large nucleoli 1 , which are surrounded by a ring of electron-dense heterochromatin . This heterochromatin contains the genes for the nucleolus organizer. The heterochromatin layer along the inner nuclear membrane or the nuclear lamina shows several gaps, thus forming nuclear pores .

Round cell nucleus (detail section) to illustrate the nuclear membrane. In light microscopy, cell nuclei are surrounded by a darkly stained line, which represents the nuclear membrane. This nuclear membrane consists of two cytomembranes , which separate the karyoplasm from the hyaloplasm. Between the two membranes is the 20–50 nm wide perinuclear space, the perinuclear cisterna 1 , which communicates with the vesicular spaces between the endoplasmic reticulum membranes. The outer nuclear membrane is confluent with the endoplasmic reticulum and shows membrane-bound ribosomes. The perinuclear cisterna is perforated by nuclear pores, which form pore complexes . Their width is about 30–50 nm, and they are covered with a diaphragm. At these covered pores, the outer and inner nuclear membrane lamellae merge. In the adjacent cytoplasm, close to the nuclear membrane, are cisternae of the granular endoplasmic reticulum 2 . The inner lamella of the nuclear membrane is covered with electron-dense material. This is heterochromatin, which is localize d at the inner nuclear lamina 3 .
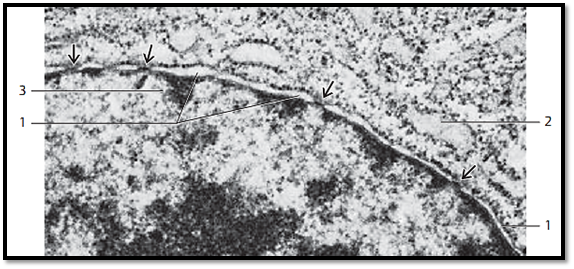
Tangential section through the surface of a cell nucleus. Note the pores in the nuclear membrane . A look in the direction of the chromatin at the inner nuclear membrane shows a ring-shaped osmophilic area with coarse granules. There is no heterochromatin close to the round cell pores. In the adjacent cytoplasm are mitochondria 1 and rough endoplasmic reticulummembranes 2 .
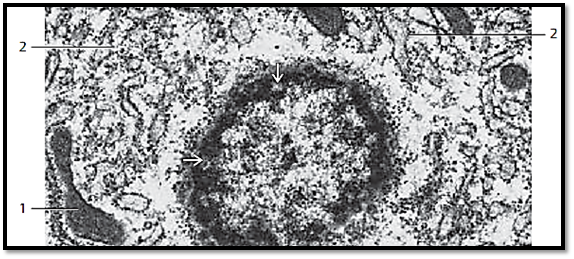
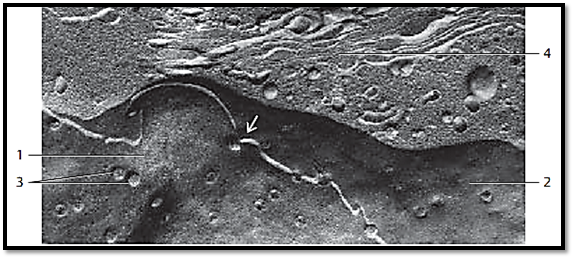
Cell nucleus and adjacent cytoplasm from an enterocyte (jejunum) in a freeze-fracture plane (cryofracture, freeze-etching), which renders a prof ile view of the nuclear membranes. The view is on the inner side of the inner lamella of the inner nuclear double membrane 1 . The white fracture line in this figure corresponds to the perinuclear cisterna. The lower plane 2 gives a view of the inner side of the inner lamella of the outer nuclear double membrane. Note the abundance of nuclear pores 3 , which allow the intracellular transport of materials between nucleus and cytoplasm. Note that the two nuclear membranes merge at the pore region. Above the nucleus are vesicles of various sizes and an array of Golgi membranes 4 .
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgar t · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


