
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 3-8-2016
3-8-2016
 1915
1915
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
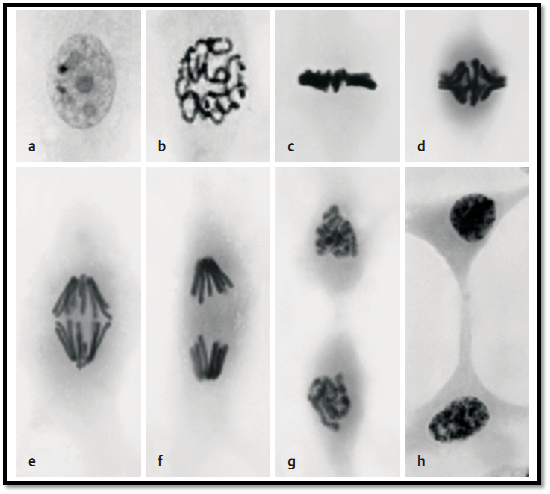
The most common type of nuclear cell division is mitosis. Mitosis yields two genetically identical daughter nuclei. It is followed by cell division ( cytokinesis). The inactive period between active periods of cell division is called interphase. Nuclear division and cell division are the high points of the cell cycle. This cycle is segmented into the phases G1, S, G2 and mitosis. Mitosis is complete d in six consecutive steps. The figure on the right presents different stages of mitosis. The dividing cells were Indian muntjac fibroblasts in cell culture ( Muntiacus muntjac ).
a) Interphase. Phase between divisions. The chromatin is dispersed or forms small aggregates. It is often possible to distinguish between highly con-dense d chromatin, called heterochromatin, and less densely packed chromatin, called euchromatin. One or two nucleoli are routinely present.
b) Prophase. Begin of mitosis. The chromatin condenses to form chromosomal threads, which b ecome increasingly thicker and shorter (coil stage, spirem). The nucleolus dissolves and the nuclear membrane falls apart.
The nuclear spindle forms and provides the apparatus for chromosome movement. The nuclear membrane dissolves in the following prometa-phase.
c) Metaphase. The chromosomes are arranged in the equatorial plane of the spindle, the metaphase plane. It now becomes apparent that there are two identical sister chromatids in each chromosome. Each chromatid has an area for the attachment to one of the spindle fibers, which extends to both spindle poles. This is the stage when karyotyping works best.
d-f) Anaphase. The two identical sister chromatids separate and move to the cell pole. Phase of the double (daughter) stars or diaster. In a later ana-phase stage, a cytokinetic actin ring forms in the position of the equatorial plane.
g) Telophase. Completion of the nuclear division. The chromatids combine and form a coil. A new nuclear membrane forms, the cytoplasm divides by contracting the cytokinetic actin ring (division ring) ( cytokinesis ). Anew cell wall is synthesized in the place of the cytokinetic actin ring.
h) Interphase.
References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


