
Lysosomes
 المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
المؤلف:
Kuehnel,W
 المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
المصدر:
Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 2-8-2016
2-8-2016
 4732
4732
Lysosomes
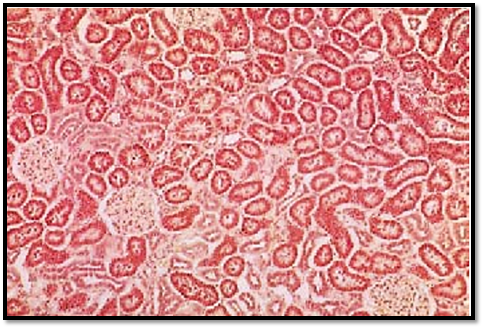
C. de Duve identified lysosomes as unique cell organelles relatively late—only in 1955. Their membrane-contained bodies are rich in acid hydrolases with pH-optima between 4.5 and 5.0. These enzymes are specific to lysosomes and can be use d as marker enzymes. Histochemical identification of these marker enzymes allows it to localize and visualize lysosomes using light microscopy. Due to their acid hydrolase content, lysosomal cell compartments play an important role in the intracellular digestion or degradation of endogenous substances ( autophagy) and phagocytosed substances (hetero-phagy). Lysosomes store insoluble metabolites and participate in the auto-lysis of cells. This figure shows cells from the adrenal gland . Four glomeruli and numerous sections through different parts of the urinary tubules are visible. The epithelial cells from these tubules contain different numbers of red-stained granular bodies. These represent lysosomes, which contain acid phosphatase, the marker enzyme for this organelle. Bur stone histochemical acid phosphatase stain.
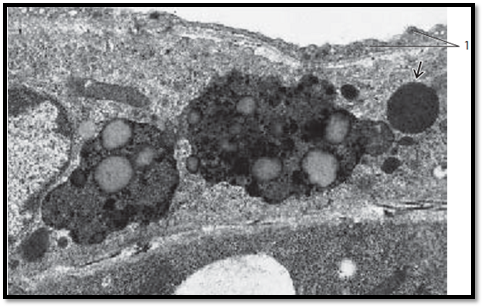
In electron microscopy, lysosomes appear as membrane-enclose d bodies of varied geometry. Their sizes are 0.1–1.2 μm. Before lysosomes participate in intracellular digestive functions, they contain only lysosomal enzymes. At that stage, they are called primary lysosomes or lysosomal transport vesicles . They arise from the trans-face of the Golgi apparatus. Primary lysosomes are able to fuse with phagocytotic vacuoles (phagosomes, autophagosomes, or heterophagosomes , respectively). These vacuoles contain substances, which must be digested. The fusion leads to cytolysosomes ( autophagolysosomes or heterophagolysosomes), commonly called secondary lysosomes . The figure shows two phagolysosomes with many ingested granules and vacuoles with different content. There is also a primary lysosome . Lysosomes are also referred to as the lytic (acid) cell compartment. Pericyte from a capillary.
1 Endothelium of a capillary
Telophagolysosome ( residual body ) in a human cell from the submandibular gland, with heteromorphic content. Lipofuscin granules, which are seen in some cell types , represent tertiary (permanent) lysosomes ( residual lysosomes, telolysosomes ). In contrast, the rod or disk-shape d granules in neutrophil granulocytes and the discus-shaped granules with crystalloid content in eosinophil granulocytes are primary lysosomes.
1 Secretor y granules
2 Granular ER (rER) membranes

References
Kuehnel, W.(2003). Color Atlas of Cytology, Histology, and Microscopic Anatomy. 4th edition . Institute of Anatomy Universitätzu Luebeck Luebeck, Germany . Thieme Stuttgart · New York .
 الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
الاكثر قراءة في علم الخلية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


