
Voting Systems-Point Methods
 المؤلف:
W.D. Wallis
المؤلف:
W.D. Wallis
 المصدر:
Mathematics in the Real World
المصدر:
Mathematics in the Real World
 الجزء والصفحة:
177-178
الجزء والصفحة:
177-178
 16-2-2016
16-2-2016
 2208
2208
Pointscore methods have often been used in sporting contests. For example, they are commonly used in track meets and in motor racing. When the Olympic Games are being held, many newspapers publish informal medal tallies to rank the performance of the competing nations—the usual method is to allocate three points for a gold medal, two for a silver, one for a bronze, and then add.
In general, a fixed number of points are given for first, second, and so on. The points are totaled, and the candidate with the most points wins. If there are n competitors, a common scheme is to allocate n points to first, n − 1 to second, ..., or equivalently n−1 to first, n−2 to second, . . . . This case, where the points go in uniform steps, is called a Borda count.
One often see scales like 5, 3, 2, 1, where the winner gets a bonus, or 3, 2, 1, 0, 0, . . . (that is, all below a certain point are equal). Sometimes more complicated schemes are used; for example, in the Indy Racing League, the following system has been used:

Pointscore methods are occasionally employed for elections, most often for small examples such as selection of the best applicant for a job.
Sometimes the result depends on the point scheme chosen.
Sample Problem 1.1 What is the result of an election with preference table
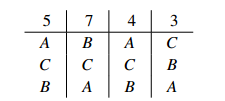
if a 3, 2, 1 count is used? What is the result if a 4, 2, 1 count is used?
Solution. With a 3, 2, 1 count the totals are A : 37,B : 36,C : 41, so C wins. With a 4, 2, 1 count the totals are A : 46,B : 43,C : 44, and A wins.
 الاكثر قراءة في الرياضيات التطبيقية
الاكثر قراءة في الرياضيات التطبيقية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


