

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Course audits
المؤلف:
Chris Dillon & Catherine Reuben & Maggie Coats & Linda Hodgkinson
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P284-C24
2025-07-22
596
Course audits
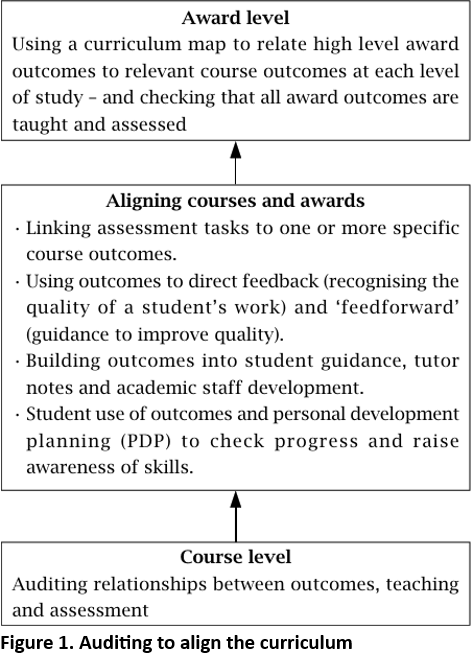
Audit is a way of checking the match between course learning outcomes and assessment. The LOTA approach put an emphasis on transparency; the work showed that auditing assessment and teaching material against the intended learning outcomes identifies gaps between:
• the intended learning outcomes and the assessment of those outcomes;
• what is assessed and what is taught; what is actually assessed and what is assumed to be assessed;
• the information and guidance given to students and that given to tutors.
Auditing was carried out by experienced ALs working as consultants to course teams. This brought a degree of independence to the process and highlighted gaps between the assumptions of the course designers and the actualities of course delivery. Addressing those gaps suggested ways the assessment and feedback process might be improved and used to enhance learning:
• Assessment tasks should be linked explicitly to relevant learning outcomes. That is, assessment needs to be specifically devised to match the relevant outcomes. Assessment should provide opportunities for important outcomes to be revisited several times during a course, and feedback to students should make reference to this.
• Recognize the developmental aspect of assessment by explaining to students the assessment strategy of a course and how they can use it to support their own learning. Opportunities for self-assessment against the learning outcomes are as important as summatively assessed tasks, and help support the development of the student as an independent learner.
• Use outcomes as criteria to prompt feedback and 'feedforward' comments from tutors. Feedback addresses existing students' performance while feedforward offers guidance to improve performance.
• Use the language of outcomes in student guidance (including course, program and qualification descriptors), notes for tutors and staff development activities as a way of talking about expectations, development and achievement.
• Support students in using outcomes in self-assessment and personal development planning (PDP) activities and encourage them to see outcomes as a way of describing their achievements to others, such as employers.
Figure 1 summarizes the audit process and links audit to curriculum alignment. In the highly modular course environment of the Open University explicitly linking outcomes, assessment, courses and awards is important. As adults already in employment many OU students will expect to use their studies and qualifications to improve their careers. Typically a student may spend about six years studying part-time with the OU.
Within that time personal goals, prospects and job opportunities may change. Waiting until the end of their degree before changing or developing their career may not be a realistic option. To take advantage of new career opportunities as and when they arise, therefore, students need to be able to talk about, and give examples of, the skills and knowledge they are gaining during their studies. In a competitive job market students may be disadvantaged if they are not able to be clear to others about their wider skills as well as their detailed subject knowledge. Learning outcomes offer concise statements to help students describe their learning.
Assessment provides milestones and checkpoints for the student to monitor and evaluate their progress against the learning outcomes. It also provides examples of applications of skills and attributes - for example: planning; time management; finding, selecting, organizing and using information; effective communication; and independent learning - that the student can draw on to provide evidence of their achievements.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















