

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences

Clauses

Part of Speech


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Flapping
المؤلف:
David Odden
المصدر:
Introducing Phonology
الجزء والصفحة:
20-2
24-3-2022
1362
Flapping
We now turn to another rule. A phonetic characteristic of many North American dialects of English is “flapping,” where /t/ and /d/ become the flap [ɾ] in certain contexts, for example in [ˈwaɾɹ̩] water. It is clear that there is no contrast between the flap [ɾ] and any other consonant of English: there are no minimal pairs such as hypothetical [hɪt] and *[hɪɾ], or *[bʌtɹ̩] and [bʌɾɹ̩], whose existence would establish that the flap is a distinct phoneme of English. Moreover, the contexts where the flap appears in English are quite restricted. In our previous examples of nonaspiration in the context ˈvCv in (4) and (6), no examples included [t] as an intervocalic consonant. Now consider the following words:

In (8a) orthographic is phonetically realized as the flap [ɾ] in the context ˈV_V, that is, when it is followed by a vowel or syllabic sonorant – represented as V – and preceded by a stressed vowel or syllabic sonorant. Maybe we have just uncovered an orthographic defect of English, since we have no letter for a flap (just as no letter represents /θ/ vs. /ð/) and some important distinctions in pronunciation are lost in spelling. The second set of examples show even more clearly that underlying t becomes a flap in this context. We can convince ourselves that the verbs [hɪt], [pʊt] and [sεt] end in [t], simply by looking at the uninflected form of the verb, or the third-person-singular forms [hɪts], [pʊts] and [sεts], where the consonant is pronounced as [t]. Then when we consider the gerund, which combines the root with the suffix -ɪŋ, we see that /t/ has become the flap [ɾ]. This provides direct evidence that there must be a rule deriving flaps from plain /t/, since the pronunciation of root morphemes may actually change, depending on whether or not the rule for flapping applies (which depends on whether a vowel follows the root).
There is analogous evidence for an underlying /t/ in the word [ˈæɾm̩ ] atom, since, again, the alveolar consonant in this root may either appear as[ th ] or [ɾ], depending on the phonetic context where the segment appears. Flapping only takes place before an unstressed vowel, and thus in /ætm̩ / the consonant /t/ is pronounced as [ɾ]; but in the related form [əˈt h amɪk] where stress has shifted to the second syllable of the root, we can see that the underlying /t/ surfaces phonetically (as an aspirate, following the previously discussed rule of aspiration).
We may state the rule of flapping as follows: “an alveolar stop becomes a flap when it is followed by an unstressed syllabic and is preceded by a vowel or glide.” You will see how vowels and glides are unified in the next chapter: for the moment, we use the term vocoid to refer to the phonetic class of vowels and glides. It is again important to note that the notion of “vowel” used in this rule must include syllabic sonorants such as [ɹ̩] for the preceding segment, and [ɹ̩] or [m̩ ] for the following segment. The rule is formalized in (9).
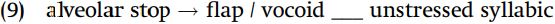
Flapping is not limited to the voiceless alveolar stop /t/: underlying /d/ also becomes [ɾ] in this same context.

 الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
الاكثر قراءة في Phonology
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















