

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Heads and modifiers revisited For and against verb phrases
المؤلف:
Jim Miller
المصدر:
An Introduction to English Syntax
الجزء والصفحة:
113-10
3-2-2022
2106
Heads and modifiers revisited
For and against verb phrases
In this short chapter, we pick up additional topics to do with dependency relations and constituent structure. The outcome of our earlier discussion was that every phrase has a central word which controls the other words, phrases and even clauses that occur in it. The central word is the head and the other words and phrases are its modifiers, which typically occur next to their head. Such phrases ‘move around’ together, can be replaced by a single word and can be ellipted. These points are illustrated in (1).
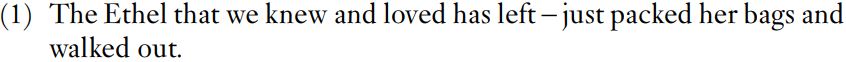 As a proper noun, Ethel typically does not allow the definite article the. Proper nouns do allow definite articles, however, provided they are also modified by a relative clause. Presumably the speaker who utters (1) is thinking of Ethel not as a single individual but as a bundle of individuals or personae who appear and disappear depending on the situation. The phrase the Ethel that we knew and loved picks out one of these individuals (as opposed, say, to the Ethel that ate administrative staff for breakfast). In the lexicon, we must include information about the subcategorization of proper nouns, that they do allow a definite article but only along with a relative clause. Ethel is the head of the noun phrase the Ethel that we knew and loved; inside the noun phrase, it controls the occurrence of the word the and the relative clause that we knew and loved.
As a proper noun, Ethel typically does not allow the definite article the. Proper nouns do allow definite articles, however, provided they are also modified by a relative clause. Presumably the speaker who utters (1) is thinking of Ethel not as a single individual but as a bundle of individuals or personae who appear and disappear depending on the situation. The phrase the Ethel that we knew and loved picks out one of these individuals (as opposed, say, to the Ethel that ate administrative staff for breakfast). In the lexicon, we must include information about the subcategorization of proper nouns, that they do allow a definite article but only along with a relative clause. Ethel is the head of the noun phrase the Ethel that we knew and loved; inside the noun phrase, it controls the occurrence of the word the and the relative clause that we knew and loved.
That whole sequence of words can be replaced by the single word she. The phenomenon of ellipsis is shown in the second clause just packed her bags and left. This clause has no subject; if there were one, it would be she or the Ethel that we knew and loved. Either the long sequence of words is replaced by a pronoun or it is ellipted, as in the second clause above.
We looked at examples of noun phrases, prepositional phrases – in the garden, adjective phrases – very difficult, and adverb phrases – amazingly quickly. On the lexicon, we adopted the idea that the verb is the head of the clause and controls all the other constituents in the clause, including the subject noun, which we treated as a complement of the verb. Many descriptions of English use a type of phrase known as the verb phrase. In (1), the subject noun phrase is The Ethel that we knew and loved and the verb phrase would be has left. Other descriptions of English do not recognize verb phrases (and in many languages other than English the concept of verb phrase is not obviously applicable).
The difficulty is that the criteria for recognizing phrases do not apply straightforwardly to English clauses. The strongest criteria are transposition and substitution. For all other types of phrase, these criteria apply without difficulty inside clauses and in common constructions. But they do not apply to sequences of finite verb plus object(s) of some kind. It used to be thought that the occurrence of do so counted as a criterion. An example is in (2).
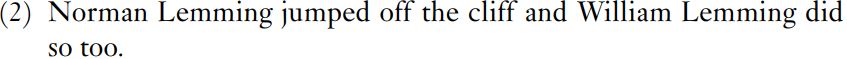 Did so indeed substitutes for jumped off the cliff, but two words are involved, and it seems clear that the verb did substitutes for jumped and that so substitutes for the complements of jumped. Example (2) is the sort of example that turns up in discussions of American linguists, but it is not the normal construction in British English, where (3) is the common construction. In (3), the sequence is so did, which is not even a straightforward substitution of did for jumped and so for off the cliff because the verb and its complement would have to be transposed to yield so did.
Did so indeed substitutes for jumped off the cliff, but two words are involved, and it seems clear that the verb did substitutes for jumped and that so substitutes for the complements of jumped. Example (2) is the sort of example that turns up in discussions of American linguists, but it is not the normal construction in British English, where (3) is the common construction. In (3), the sequence is so did, which is not even a straightforward substitution of did for jumped and so for off the cliff because the verb and its complement would have to be transposed to yield so did.
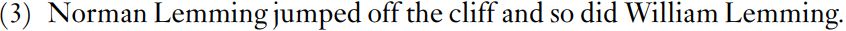 The one structure from spontaneous spoken English that might fit is shown in (4).
The one structure from spontaneous spoken English that might fit is shown in (4).
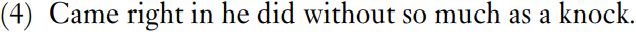
Unfortunately, the structure of (4) is not clear. Came right in he did could be seen as a rearrangement of He did come right in; except that in the latter come has no tense, whereas in (4) came is past tense. Moreover, new electronic bodies of spoken English are yielding examples such as They complained about it all the time they did which has two clauses, They complained about it all the time and the tagged-on clause they did. So (4) can be analyzed as having a two-clause structure in which the first clause, as happens regularly in spontaneous speech, is lacking a subject. That is, (4) is not a basic construction but results from ellipsis.
Other arguments for verb phrases turn on examples of the sort in (5) and (6)
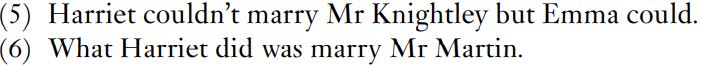
The argument is that in (5) the phrase marry Mr Knightley has been ellipted – Emma could marry Mr Knightley is reduced to could. In (6), was has the WH clause What Harriet did as its subject and marry Mr Knightley as its complement. That is, the sequence marry Mr Knightley turns up in different slots, and in (6) can even be genuinely transposed to the front to give (7).
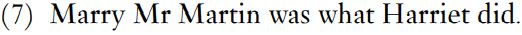
These examples show that a verb plus complements (and adjuncts) does form a phrase in certain constructions, but the argument does not apply to has left in (1), with a verb marked for tense. Only verbs without tense and aspect turn up freely in different constructions. One piece of data that looks more promising for verb phrases is conjunction, as in (8).
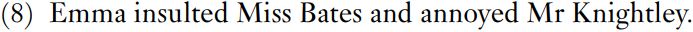
Example (8) can be analyzed as having a subject noun phrase, Emma, and two phrases – verb phrases – connected by and: insulted Miss Bates and annoyed Mr Knightley. There are, however, alternative analyses that treat the supposed verb phrases as clauses whose subject noun phrase has been ellipted, and other analyses try to handle conjunction in terms of heads and their dependent modifiers rather than in terms of phrases. Although many analyses employ verb phrases, the evidence is much weaker than for other types of phrase and not strong enough for us to abandon the view that the verb is the head of the clause.
 الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















