

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Transposition
المؤلف:
Jim Miller
المصدر:
An Introduction to English Syntax
الجزء والصفحة:
13-2
28-1-2022
2157
Transposition
Many sequences of words can be moved together into different slots in a clause; this is evidence that the words form a phrase. Let us go back to (3a), Jeeves shimmered into the room. We can think of (3a) as being converted to (3c) by the words into the room being moved, or transposed, to the front of the clause. This transposition indicates that the three separate words combine into a larger block, a phrase. Transposition also applies to phrases without prepositions. The words the results in (5) can be moved to the front of the clause to give The results Barbara handed to Alan on Tuesday, a clause that is appropriate if the speaker or writer continues, for example, The actual scripts she kept until Friday.
The above examples of transposition have to do with a sequence of words being moved from one position in a clause to another position without any other changes in the clause. (Remember the comment ,that the clause is a unit of analysis within which we can talk coherently about the order of phrases and the fact that phrases can occupy different positions.) Transposition is one of the tests that reveal whether a given sequence of words make up a phrase or are just words that happen to come one after the other. If you know English well, you may be tempted to think that such a test is unnecessary; but two facts speak against this temptation. One is that in spite of the vast amount of research on English syntax in the twentieth century we still come across examples whose structure is not obvious. The second fact is that many linguists work not just on languages other than English but on languages which have been little studied or not studied at all. In these circumstances, tests such as transposition are essential.
The test of transposition is also applied in a slightly different fashion. Consider the active clause in (6a) and the passive clause in (6b).
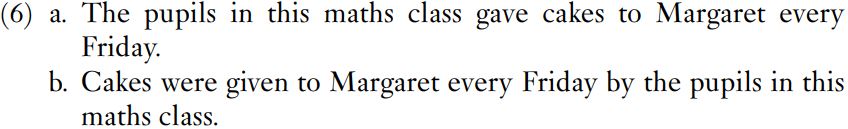 The phrase the pupils in this math class is at the beginning of the clause in (6a) and refers to the people doing the giving. The same sequence is at the end of the clause in (6b) and is the complement of the preposition by. In contrast with (3a) and (3b), the differences between (6a) and (6b) consist of more than just a group of words being moved from one position to another. Example (6a) contains gave, while (6b) contains the words were and given. Example (6b) also contains the prepositional phrase by the pupils in this math class, whereas (6a) has no prepositional phrase. When we use ‘transposition’ with respect to examples such as (6a) and (6b), we are talking about sequences of words that turn up in a particular order in one position in one construction and about the same sequences of words turning up in the same order in another construction. The sequence the pupils in this math class occurs in the different constructions in (6a) and (6b).
The phrase the pupils in this math class is at the beginning of the clause in (6a) and refers to the people doing the giving. The same sequence is at the end of the clause in (6b) and is the complement of the preposition by. In contrast with (3a) and (3b), the differences between (6a) and (6b) consist of more than just a group of words being moved from one position to another. Example (6a) contains gave, while (6b) contains the words were and given. Example (6b) also contains the prepositional phrase by the pupils in this math class, whereas (6a) has no prepositional phrase. When we use ‘transposition’ with respect to examples such as (6a) and (6b), we are talking about sequences of words that turn up in a particular order in one position in one construction and about the same sequences of words turning up in the same order in another construction. The sequence the pupils in this math class occurs in the different constructions in (6a) and (6b).
The test of transposition applies to other sequences of words, as shown by (7).

In (7a), the sequence of words/the phrase very heavy is the complement of is; in (7b) it is the modifier of parcel. It turns up at the beginning of the spoken construction in (7c). In (7d) it is also the complement of is, but in a special emphatic construction. Very can be replaced by words such as astonishingly, and the sequence can be made longer – astonishingly and frighteningly heavy – but can still be transposed, as shown in This parcel is astonishingly and frighteningly heavy, this astonishingly and frighteningly heavy parcel was delivered yesterday, What this parcel is is astonishingly and frighteningly heavy
Examples (3a) and (3c) show that a sequence of words introduced by a preposition – into the room – can be transposed. Another example is given in (8).
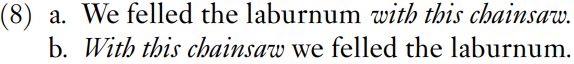
 الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
الاكثر قراءة في Syntax
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















