

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners

Direct and Indirect speech


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Comparative and Superlative
المؤلف:
DICTIONARYCAMBRIDGE.ORG
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
7-6-2021
1489
Comparison: adjectives (bigger, biggest, more interesting)
Comparative and superlative adjectives
Comparative adjectives
Comparative adjectives compare one person or thing with another and enable us to say whether a person or thing has more or less of a particular quality:
Josh is taller than his sister.
I’m more interested in music than sport.
Big cars that use a lot of petrol are less popular now than twenty years ago.
Superlative adjectives
Superlative adjectives describe one person or thing as having more of a quality than all other people or things in a group:
The ‘Silver Arrow’ will be the fastest train in the world when it is built.
The most frightening film I’ve ever seen was Alfred Hitchcock’s ‘Psycho’.
What is the least expensive way of travelling in Japan?
Comparative or superlative?
A comparative compares a person or thing with another person or thing. A superlative compares a person or thing with the whole group of which that person or thing is a member:
Joe’s older than Mike. (comparing one person with another)
Sheila is the youngest girl in the family. (comparing one person with the whole group she belongs to)
When there are just two members in a group, traditionally, we use the comparative. However, in informal situations people often use the superlative:
Who is younger, Rowan or Tony? (traditional usage)
Jan and Barbara are both tall, but Jan’s the tallest. (more informal)
Comparative and superlative adjectives: form
One-syllable adjectives (big, cold, hot, long, nice, old, tall)
To form the comparative, we use the -er suffix with adjectives of one syllable:
It’s colder today than yesterday.
It was a longer holiday than the one we had last year.
Sasha is older than Mark.
To form the superlative, we use the -est suffix with adjectives of one syllable. We normally use the before a superlative adjective:
I think that’s the biggest apple I’ve ever seen!
At one time, the Empire State building in New York was the tallest building in the world.
They have three boys. Richard is the oldest and Simon is the youngest.
Spelling of comparatives and superlatives with one-syllable adjectives
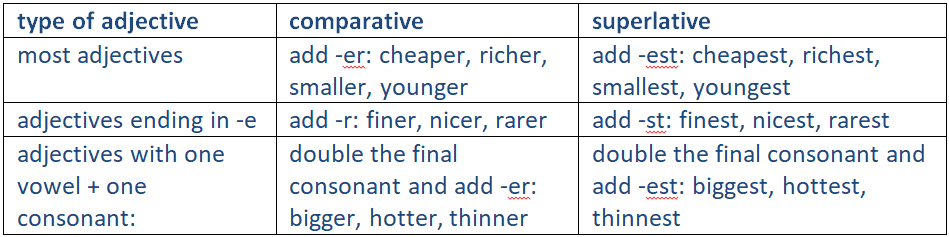
One-syllable adjectives which are irregular
Some one-syllable adjectives have irregular comparative and superlative forms:
1-bad, worse, worst far, farther/further, farthest/furthest
2-good, better, best old, older/elder, oldest/eldest
The morning flight is better than the afternoon one.
His elder sister works for the government.
Olivia is Denise’s best friend.
I think that was the worst film I’ve ever seen!
Pluto is the furthest planet from the sun in our solar system.
Warning:
We do not use more or most together with an -er or -est ending:
They emigrate because they are looking for a better life.
Not: … a more better life
The beach at Marmaris is one of the biggest in Turkey.
Not: … the most biggest …
Two-syllable adjectives
Two-syllable adjectives ending in -y change y to i and take the -er and -est endings:

We were busier last week than this week.
Are you happier now that you’ve changed your job?
That was the easiest exam I’ve ever taken.
Some other two-syllable adjectives (especially those ending in an unstressed vowel sound) can also take the -er and -est endings:

I’ve always thought that Donald was cleverer than his brother.
This new bed is narrower than the old one.
The guest bedroom is the quietest room in the house because it overlooks the garden.
We don’t normally use the -er and -est endings with two-syllable adjectives ending in -ful. Instead, we use more and most/least:
This dictionary is more useful than the one we had before.
Not: This dictionary is usefuller …
You’ll have to try to be more careful in future.
The most useful tool in the kitchen is a good sharp knife.
Not: The usefulest tool in the kitchen …
This is the least harmful chemical in terms of the environment.
Longer adjectives
Adjectives of three or more syllables form the comparative with more/less and the superlative with most/least:
The second lecture was more interesting than the first.
Not: The second lecture was interestinger …
That way of calculating the figures seems less complicated to me.
London is the most popular tourist destination in England.
Not: London is the popularest …
If you are going as a group, the least expensive option is to rent an apartment or villa.
Comparative adjectives: using much, a lot, far, etc.
We can strengthen or emphasise a comparative adjective using words such as much, a lot, far, even or rather, or by using than ever after the adjective:
This food is much better than the food we had yesterday.
The town is a lot more crowded these days because of the new shopping centre.
Alex is far less intelligent than the other kids in the class.
We’ve been busier than ever at work this last month or so.
We can soften a comparative adjective using a little or a bit. A bit is less formal:
She feels a little more confident now that she’s given her first public performance.
or She feels a bit more confident … (less formal)
Comparative adjectives: using than
We use than when we mention the second person or thing in the comparison. If the second person mentioned takes the form of a personal pronoun, we normally use the object form of the pronoun (me, you, him, her, us, them):
Could you carry this? You’re stronger than me.
Not: You’re stronger than I.
Why did you choose Robert? Marie is more experienced than him.
In more formal situations, instead of than + object pronoun, we can use than + subject pronoun + be:
You managed to answer the ten questions correctly? Well, you’re definitely cleverer than I am!
I preferred Henrietta to Dennis. She was always more sociable than he was.
Comparative adjectives: -er and -er, more and more
To talk about how a person or thing is changing and gaining more of a particular quality, we can use two -er form adjectives connected by and, or we can use more and more before an adjective. We don’t follow such comparisons with than:
The weather is getting hotter and hotter.
I’m getting more and more interested in conservation these days.
Comparative adjectives: the -er, the -er and the more …, the more …
If a person or things gains more of a particular quality and this causes a parallel increase of another quality, we can repeat the + a comparative adjective:
The colder it is, the hungrier I get. (as the weather gets colder, I get hungrier)
The more generous you are towards others, the more generous they are likely to be towards you.
Reduced forms after comparatives
After than, we often don’t repeat subject pronouns with impersonal subjects, or auxiliary verbs with passive voice verbs:
The exam results were better than predicted. (preferred to … better than people predicted.)
Temperatures that summer were higher than previously recorded. (preferred to … than were previously recorded.)
Less and not as/not so with comparatives
We use less with longer adjectives (interesting, beautiful, complicated), but we don’t normally use less with short adjectives of one syllable (big, good, high, small). Instead we use not as … as …, or not so … as … Not as is more common than not so:
The second method was less complicated than the first one.
This new laptop is not as fast as my old one. I’m sorry I bought it now. (preferred to is less fast than my old one.)
Prepositions after superlative adjectives
We don’t normally use of before a singular name of a place or group after a superlative adjective:
The castle is the oldest building in the city.
Not: The castle is the oldest building of the city …
She’s the youngest musician in the orchestra.
However, we can use of with a plural word referring to a group:
All the sisters are pretty, but Sarah’s the prettiest of them all.
The with superlative adjectives
When a superlative adjective is followed by a noun, we normally use the:
This is the best meal I’ve had for a long time.
Not: This is best meal …
In informal situations, we can often omit the after a linking verb (be, seem) or a verb of the senses (look, taste) if there is no noun:
[talking about sweaters in a shop]
They’ve got them in red, green or grey. Which looks best?
If you want to get a message to Peter, email is quickest. He never answers the phone.
Other determiners with superlative adjectives
Before a superlative adjective, we can use a possessive determiner (my, his, their), or the + a number (two, three, first, second), or a possessive determiner + a number:
My worst score ever in an exam was zero. I just couldn’t answer any of the questions.
Birmingham is the second biggest city in England.
His two best friends organized a surprise party for him on his fortieth birthday.
Emphasising superlative adjectives
We can make a superlative adjective stronger with by far, easily or of all:
The Beatles were by far the most successful rock band of the 1960s.
This method is by far the least complicated.
She’s easily the best dancer in the group. No one is as elegant as her.
There were a number of excellent poems entered for the competition, but the best poem of all was written by a ten-year-old boy.
In more formal situations, we can use quite:
This is quite the most irresponsible behaviour I have ever seen.
To-infinitives after superlative adjectives
We can use a to-infinitive after a superlative adjective, with a meaning similar to a relative clause with who, which or that:
Who was the oldest person to compete in the London Marathon of 2008? (Who was the oldest person who competed …?)
The Golden Swan was the largest sailing-ship ever to be used in battle.
Comparative adjectives: typical errors
A comparative adjective is followed by than, not that or as:
The next hotel we tried was more expensive than the first one.
Not: … more expensive that the first one … or …more expensive as the first one …
After a superlative adjective, we don’t normally use of before a singular name of a place or group:
She was the tallest girl in the team.
Not: She was the tallest girl of the team.
We use the superlative, not the comparative, when we compare more than two people or things:
Which is the city’s biggest hotel?
Not: … bigger hotel
 الاكثر قراءة في Comparative and superlative
الاكثر قراءة في Comparative and superlative
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















