
Permeability
 المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
 الجزء والصفحة:
142
الجزء والصفحة:
142
 20-4-2021
20-4-2021
 2324
2324
Permeability
Some substances cause the magnetic lines of flux to get closer together than they are in the air. Some materials can cause the lines of flux to become farther apart than they are in the air.
The first kind of material is ferromagnetic, and is of primary importance in magnetism. Ferromagnetic substances are the ones that can be “magnetized.” Iron and nickel are examples. Various alloys are even more ferromagnetic than pure iron or pure nickel.
The other kind of material is called diamagnetic. Wax, dry wood, bismuth, and silver are substances that actually decrease the magnetic flux density. No diamagnetic material reduces the strength of a magnetic field by anywhere near the factor that ferromagnetic substances can increase it.
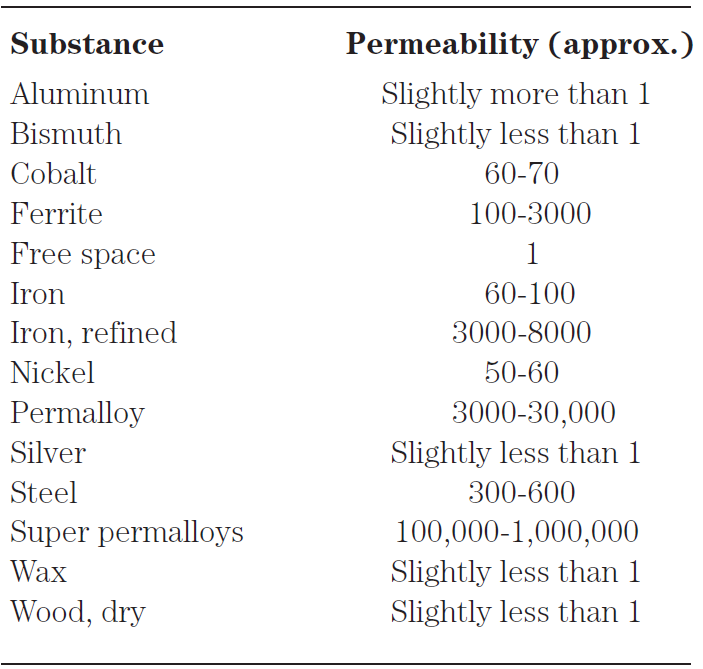
Permeability is measured on a scale relative to a vacuum, or free space. Free space is assigned permeability 1. If you have a coil of wire with an air core, and a current is forced through the wire, then the flux in the coil core is at a certain density, just about the same as it would be in a vacuum. Therefore, the permeability of pure air is about equal to 1. If you place an iron core in the coil, the flux density increases by a factor of about 60 to several thousand times. Therefore, the permeability of iron can range from
60 (impure) to as much as 8,000 (highly refined).
If you use certain permalloys as the core material in electromagnets, you can increase the flux density, and therefore the local strength of the field, by as much as 1,000,000 times. Such substances thus have permeability as great as 1,000,000.
If for some reason you feel compelled to make an electromagnet that is as weak as possible, you could use dry wood or wax for the core material. But usually, diamagnetic substances are used to keep magnetic objects apart, while minimizing the interaction between them.
Diamagnetic metals have the useful property that they conduct electric current very well, but magnetic current very poorly. They can be used for electrostatic shielding, a means of allowing magnetic fields to pass through while blocking electric fields. Table 1 gives the permeability ratings for some common materials.
Table 1. Permeability of some common materials.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


