

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Verbal Nouns
المؤلف:
GRAMMER MONSTER.COM
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
5-4-2021
7014
What Are Verbal Nouns? (with Examples)
Verbal Nouns
A verbal noun is a noun that has no verb-like properties despite being derived from a verb.
Easy Examples of Verbal Nouns
Verbal nouns are formed in a number of ways (usually by adding a suffix to the base form of the verb).
For example:
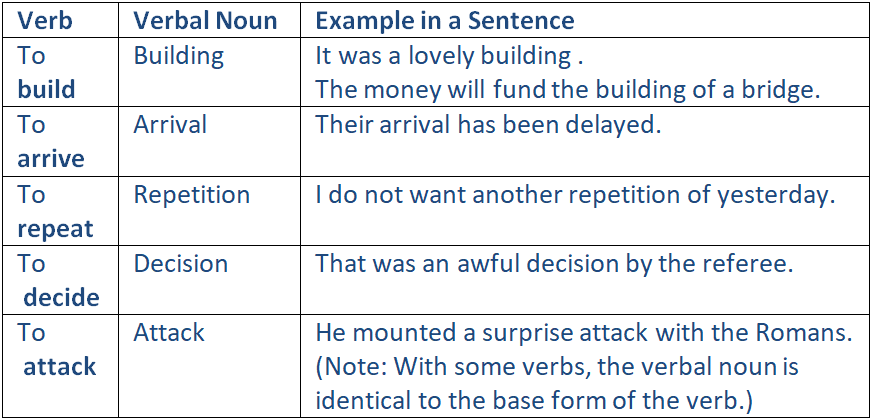
Real-Life Examples of Verbal Nouns
Being normal nouns, verbal nouns can be modified by adjectives, be pluralized (if the sense allows), and be followed by prepositional phrases (e.g., …of men, …by me).
No man saw the building of the New Jerusalem; it descended out of heaven from God (Historian John Robert Seeley)
We're seeing the arrival of conversational robots that can walk in our world. (Robot designer David Hanson)
I need to die for the killing of those people. (American serial killer Aileen Wuornos)
Malicious attacks on the Soviet Union produce a natural feeling of indignation. (Soviet politician Yuri Andropov)
The Difference between Verbal Nouns and Gerunds
Verbal nouns are not the same as gerunds (another type of noun formed from a verb).
A gerund is a noun that, having derived from a verb, retains a few verb-like properties.
For example, a gerund can be modified by an adverb and can take a direct object.
Compare these two examples. The first contains a verbal noun; the second, a gerund.
This bad drawing of a dog is not acceptable for your project.
(This is a verbal noun. It is acting just like a noun. Just as any noun could have, it has a determiner (This) and an adjective (bad), and it is followed by a prepositional phrase (of a dog).)
Badly drawing a dog is not acceptable for your project.
(This is a gerund. It is functioning as a noun, but it has two notable verb-like properties. Just as any verb could have, it has an adverb (badly) and a direct object (a dog).)
More about Verbal Nouns
For many grammarians, the term verbal noun has a much broader definition, which covers all verb-derived words that can function as nouns, such as gerunds and infinitives (both of which retain verb-like qualities).
Gerunds. All gerunds end -ing (e.g., building, arriving, killing).
Killing women and children indiscriminately revolts my soul. (Paraphrase of a quotation by US President Herbert Hoover about the atomic bomb)
(Despite being a noun, the gerund killing is showing some verb-like properties. It has taken a direct object (women and children) and is modified by an adverb (indiscriminately).)
Infinitive. The infinitive form of a verb (the form with to in front) can function as a noun.
To kill women and children indiscriminately revolts my soul.
(To kill is the infinitive form of the verb. In this example, it is functioning as a noun, just like the gerund above.)
Grammarians who prescribe to the broader definition of verbal noun often describe verbal nouns with no verb-like properties as "pure verbal nouns." Here's the same example written with a "pure verbal noun."
The indiscriminate killing of women and children revolts my soul.
(Notice that killing has the following modifiers: The (a determiner), indiscriminate (an adjective), and of women and children (a prepositional phrase). These are all good indicators that you're dealing with a pure verbal noun.)
Why Should I Care about Verbal Nouns?
Verbal nouns (or pure verbal nouns as they're sometimes called) are common in business writing because they carry an air of formality. As a result, it is not uncommon to read a sentence like this in business email:
The implementation of the new system will commence on Monday.
(This formal sentence features the pure verbal noun implementation.)
So, if you're looking for a formal tone, you could consider verbal nouns for your sentences. However, verbal nouns can also portray you as straight-laced and starchy.
Here are two good reasons to avoid verbal nouns:
(Reason #1 to Avoid a Verbal Noun) Pure verbal nouns eat up your word count.
As verbal nouns are often preceded by a or the and followed by a prepositional phrase (e.g., …of men, …about women), they are pretty inefficient from a word count perspective.
They were having a discussion about the implementation of the new rules.
(With two pure verbal nouns, this sentence has 12 words.)
They were discussing implementing the new rules.
(A simple rewording to avoid the verbal nouns cuts the word count to 7 with no loss of meaning. The efficiency is achieved by losing the articles (a and the) and by using words that can take direct objects, which kills the need for prepositions (about and of).)
(Reason #2 to Avoid a Verbal Noun) A string of pure verbal nouns does not flow naturally.
Businessmen's penchant for verbal nouns sometimes causes them to string their nouns together, creating jerky non-flowing sentences.
Your explanation of the expectations of the community was clear.
(Jerky)
You explained the community's expectations clearly.
(When you've got a string of nouns, replacing one with a verb (here, explained) is a good way to create a smoother sentence.)
Here's a good reason to use verbal nouns:
(Reason #1 to Use a Verbal Noun) A pure verbal noun can add a little emphasis.
Even though verbal nouns can sound stuffy, that air of formality can provide emphasis.The careful selection of adjectives is essential.
Selecting adjectives carefully is essential.
(With its pure verbal noun, the top version sounds more authoritative and convincing.)
 الاكثر قراءة في Verbal nouns
الاكثر قراءة في Verbal nouns
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















