
Electromagnetic deflection
 المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
 الجزء والصفحة:
44
الجزء والصفحة:
44
 5-4-2021
5-4-2021
 2288
2288
Electromagnetic deflection
Early experimenters with electricity and magnetism noticed that an electric current produces a magnetic field. This discovery was probably an accident, but it was an accident that, given the curiosity of the scientist, was bound to happen. When a magnetic compass is placed near a wire carrying a direct electric current, the compass doesn’t point toward magnetic north. The needle is displaced. The extent of the error depends on how close the compass is brought to the wire, and also on how much current the wire is carrying.
Scientific experimenters are like children. They like to play around with things. Most likely, when this effect was first observed, the scientist tried different arrangements to see how much the compass needle could be displaced, and how small a current could be detected. An attempt was made to obtain the greatest possible current-detecting sensitivity. Wrapping the wire in a coil around the compass resulted in a device that would indicate a tiny electric current (Fig. 1). This effect is known as galvanism, and the meter so devised was called a galvanometer

Fig. 1: A simple galvanometer. The compass must lie flat.
Once this device was made, the scientist saw that the extent of the needle displacement increased with increasing current. Aha—a device for measuring current!
Then, the only challenge was to calibrate the galvanometer somehow, and to set up some kind of standard so that a universal meter could be engineered. You can easily make your own galvanometer. Just buy a cheap compass, about two feet of insulated bell wire, and a six-volt lantern battery. Set it up as shown in Fig. 1. Wrap the wire around the compass four or five times, and align the compass so that the needle points right along the wire turns while the wire is disconnected from the battery.
Connect one end of the wire to the minus (–) terminal of the battery. Touch the other end to the plus (+) terminal, intermittently, and watch the compass needle. Don’t leave the wire connected to the battery for any length of time unless you want to drain the battery in a hurry.
You can buy a resistor and a potentiometer at a place like Radio Shack, and set up an experiment that shows how galvanometers measure current. For a 6-V lantern battery, the fixed resistor should have a value of at least 330 Ω at 1/4 watt, and the potentiometer should have a value of 10 KΩ (10,000 Ω) maximum. Connect the resistor and potentiometer in series between one end of the bell wire and one terminal of the battery, as shown in Fig. 2. The center contact of the potentiometer should be short-circuited to one of the end contacts, and the resulting two terminals used in the circuit. When you adjust the potentiometer, the compass needle should deflect more or less, depending on the current through the wire. Early experimenters calibrated their meters by referring to the degree scale around the perimeter of the compass.
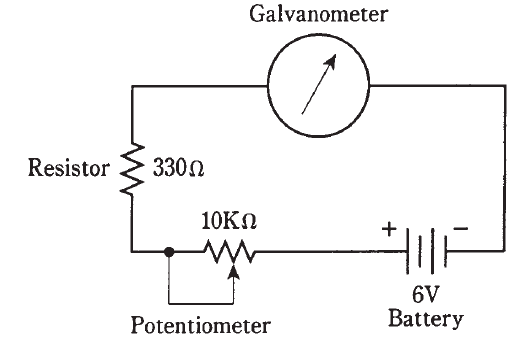
Fig. 2: Circuit for demonstrating how a galvanometer indicates relative current.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


