

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Nouns Gender
المؤلف:
COLLINS.COM
المصدر:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
2-4-2021
909
Gender of nouns - Easy Learning Grammar
In some languages, nouns have gender. This means that a noun causes other words such as adjectives to change their spelling according to certain rules. Grammatical gender has little to do with biological gender. English does not have grammatical gender for nouns.
On the other hand, the biological gender of the thing or person referred to does affect a few areas of English grammar.
a cow… she or it a bull… he or it
a girl… she a boy… he
Gender distinctions are relevant where personal pronouns (Personal pronouns) and possessive determiners (Determiners) have to be decided on. These distinctions are only noticeable in singular nouns.
He found his book.
He had been looking for it.
She found her book.
She had been looking for it.
There are also special cases, such as the association of neuter gender with babies and small animals, or feminine gender with a vehicle.
I just saw a mouse. It was running across the room.
The spider was spinning its web.
The beetle crawled into its hole.
The baby threw down its rattle.
I’ve got a new boat; she’s a real beauty.
Nouns denoting male persons and animals are masculine in that they are used with the pronouns and possessive determiners he, him, his.
Nouns denoting female persons and animals are feminine in that they are used with the pronouns and possessive determiners she, her, hers.
Barry saw Linda. He called out to her that he had found her book.
Marcia saw Paul. She called out to him that she had found his book.
Madeleine saw Kim. She said ‘Hello’ to her.
The pronouns and possessive determiners used to refer to common or neuter nouns are: it, its.
The truth will emerge. It always does.
Nouns denoting inanimate objects and abstract notions are also neuter.
Some nouns denoting people have the same form for masculine and feminine. Nouns used for a group, e.g. government or team, have common or neuter gender, even when we know that the group is made up exclusively of male or female members.
The government has changed its policy.
The team has won its first medal at a major championship.
With some nouns of common gender it might be possible to specify the gender if we had sufficient information. But if we do not have this knowledge, the choice of pronoun or possessive determiner becomes a problem.
a driver…he/she
the cook…he/she
doctor…he/she
As a way around this problem, in informal and spoken English, their is often used after a singular noun or an indefinite pronoun. See Pronouns. Some people consider this grammatically unacceptable, but it is widely used to avoid repetitions of his or her or him or her.
Each student must apply to his or her tutor for an extension.
Everyone must apply to their tutor for an extension.
Someone has left their coat in my room.
The specialized terms used to name male, female and neutered animals show a number of gender differences.
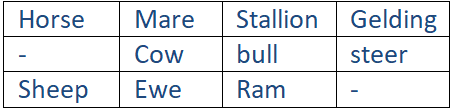
Gender differences are also shown in the nouns that indicate relationships.

Many nouns denoting an occupation have no explicit gender.
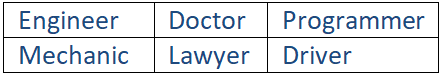
Some occupations and professions have a special feminine form for the noun.
Call your bank manager today.
Sue is manageress of a hairdressing salon.
Actors from all over the UK attended the ceremony.
Here in the studio to talk about her new book is actress Mary Farrell.
Many people prefer to avoid these forms, regarding the distinction as unnecessary.
J.K. Rowling is a highly successful author.
Judi Dench is one of our finest actors.
Michelle Stewart has been promoted to Branch Manager.
The forms authoress and poetess are now considered patronizing and are rarely used.
Some speakers prefer to use a different form of the word or an entirely different word in order to avoid a gender-marked noun.
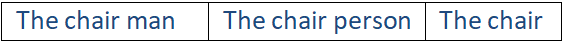
If necessary, the gender of a common noun can be made clear by adding a descriptive term such as woman or male/female.
Would you prefer to see a woman doctor?
Male staff should use locker room B.
If we are discussing a country from an emotional, economic, or political viewpoint we sometimes use feminine gender.
 الاكثر قراءة في Nouns gender
الاكثر قراءة في Nouns gender
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















