
Present Perfect Continuous
 المؤلف:
EF.COM
المؤلف:
EF.COM
 المصدر:
...
المصدر:
...
 الجزء والصفحة:
...
الجزء والصفحة:
...
 25-3-2021
25-3-2021
 1792
1792
Present perfect continuous
The present perfect continuous is used to refer to an unspecified time between 'before now' and 'now'. The speaker is thinking about something that started but perhaps did not finish in that period of time. He/she is interested in the process as well as the result, and this process may still be going on, or may have just finished.
Actions that started in the past and continue in the present
She has been waiting for you all day (= and she's still waiting now).
I've been working on this report since eight o'clock this morning (= and I still haven't finished it).
They have been travelling since last October (= and they're not home yet).
Actions that have just finished, but we are interested in the results
She has been cooking since last night (= and the food on the table looks delicious).
It's been raining (= and the streets are still wet).
Someone's been eating my chips (= half of them have gone).
Forming the present perfect continuous
The present perfect continuous is made up of two elements: the present perfect of the verb 'to be' (have/has been), and the present participle of the main verb (base+ing)
|
Subject
|
+has/have been
|
+base +ing
|
|
She
|
Has been
|
swimming
|
Affirmative: She has been / She's been running.
Negative: She hasn't been running.
Interrogative : Has she been running?
Interrogative negative: Hasn't she been running?
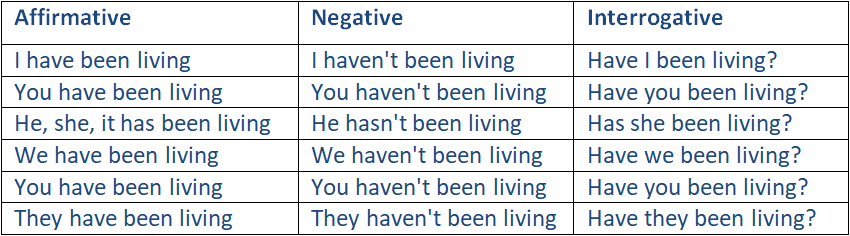
Example: present perfect continuous, TO LIVE
Verbs without continuous forms
With verbs not normally used in the continuous form, use the simple present perfect instead (verbs such as: know, hate, hear, understand, want).
I've wanted to visit China for years.
She's known Robert since she was a child.
I've hated that music since I first heard it.
I've heard a lot about you recently.
We've understood everything.
 الاكثر قراءة في Present Perfect Continuous
الاكثر قراءة في Present Perfect Continuous
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


