

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Potentiometric Biosensors
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
الجزء والصفحة:
20-1-2021
2249
Potentiometric Biosensors
Changes in ionic concentrations are easily determined by use of ionselective electrodes. This forms the basis for potentiometric biosensors. Many biocatalysed reactions involve charged species, each of which will
Table 1. Biocatalytic reactions that can be used with ion-selective electrode biosensors.
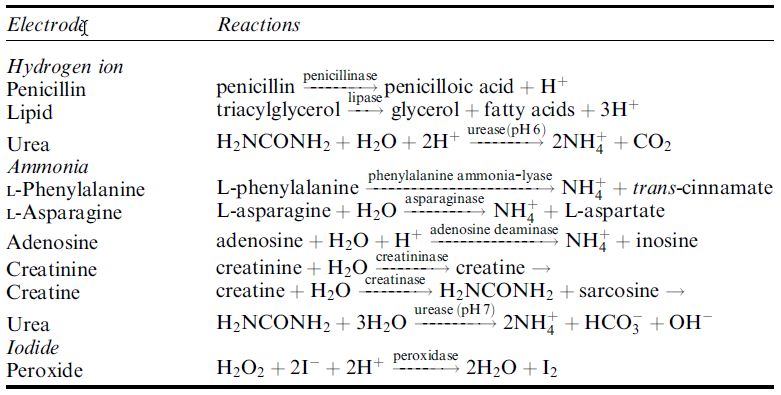

Figure 1. A FET-based potentiometric biosensor.
absorb or release hydrogen ions according to their pKa and the pH of the environment. This allows a relatively simple electronic transduction using the commonest ion selective electrode, the pH electrode. Table 1. shows some biocatalytic reactions that can be utilised in potentiometric biosensors. Potentiometric biosensors can be miniaturised by the use of field effect transistors (FETs).
Ion-selective field effect transistors (ISFETs) are low-cost devices that are in mass production. Figure 1. shows a diagrammatic cross-section through an npn hydrogen ion-responsive ISFET with an approximately 0.025mm2 biocatalytic membrane covering the ion-selective membrane.
The build-up of positive charge on this surface (the gate) repels the positive holes in the p-type silicon, causing a depletion layer and allowing the current to flow. The reference electrode is usually an identical ISFET without any biocatalytic membrane. A major practical problem with the manufacture of such enzyme-linked FETs (ENFETs) is protection of the silicon from contamination by the solution, hence the covering of waterproof encapsulant. Because of their small size, they only require minute amounts of biological material and can be produced in a form whereby they can determine several analytes simultaneously. A further advantage is that they have a more rapid response rate compared with the larger, sluggish ion-selective electrode devices. The enzyme may be immobilised to the silicon nitride gate using polyvinylbutyral deposited by solvent evaporation and cross-linked with glutaraldehyde. Such devices still present fabrication problems such as reproducibility, drift, sensitivity to light and the need for on-chip temperature compensation.
Use of membranes selective for ions other than hydrogen ions, such as ammonium, allows many related biosensors to be constructed. Potentiometric biosensors for DNA have been developed which use anti-DNA monoclonal antibodies conjugated with urease. DNA is bound to a membrane, placed on the electrode and quantified by the change in pH on addition of urea .
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















