
Chromatography
 المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
المؤلف:
John M Walker and Ralph Rapley
 المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
المصدر:
Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 5th Edition
 الجزء والصفحة:
الجزء والصفحة:
 15-1-2021
15-1-2021
 1398
1398
Chromatography
The major step(s) in most downstream processes is purification of the target molecule by chromatography. There are four main chromatographic techniques used for the purification of proteins: ion-exchange, affinity, gel filtration and hydrophobic interaction. The principle of each, examples and the usual stage at which they are used during downstream processing are detailed in Table .1. Of the four, ionexchange, affinity and hydrophobic interaction chromatography are adsorptive processes whereby binding and elution are undertaken. The use of adsorptive chromatographic processes for downstream processing, the constraints upon this type of chromatography and future outlook have been reviewed by Lydiatt.
Table .1 Details of the four major chromatographic methods used for downstream processing of biologics.
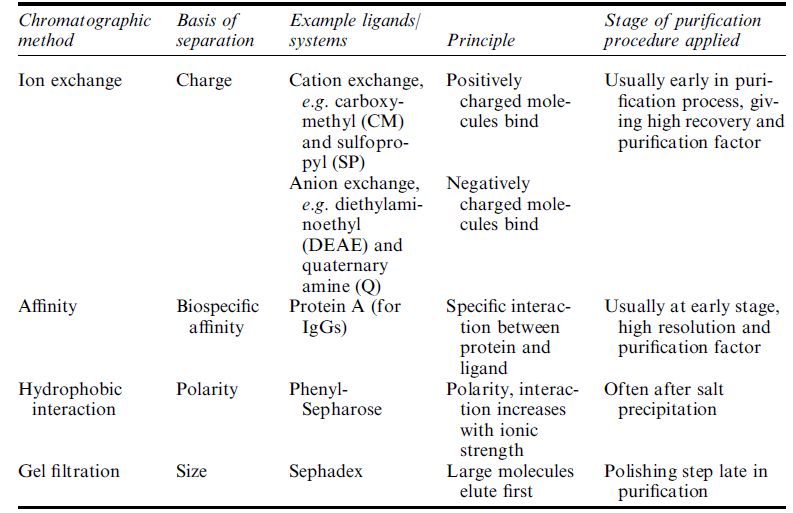
The selection of which type of chromatography/approach to use, and when, is much more complicated than perhaps might be expected from Table 1. The scalability of the system, binding capacity for adsorptive approaches, flow rates, resolution, pH, ionic strengths, costs and monitoring of the process are among a few of the variables that must be considered before design of the system and ultimate scale-up operation. Another important consideration is the chromatography matrix itself, and ideally this should be:
- reusable;
- chemically stable (not leach during processing);
- physically stable (i.e. withstand the required flow conditions);
- have appropriate internal structure/porosity to give suitable mass transfer and capacity;
- be commercially available from a reliable source to meet regulatory requirements;
- be cost effective.
Typical matrix types often encountered include agarose and crosslinked agaroses, cross-linked dextran, composites of dextran and polyacrylamide or dextran and agarose, cellulose and organic polymer-based beads.
A survey of approximately 100 papers in the primary literature where the four chromatographic approaches outlined above have been utilised confirms that affinity chromatography achieves the highest purification factors of all these approaches (Table.2). However, ion-exchange chromatography is the most commonly utilised chromatographic approach, comprising approximately 41% of all purification steps used, and gel filtration chromatography (17%) is the second most widely used approach. Precipitation is used almost exclusively as a first step (Figure .2), whereas ion exchange is used as a bulk purification step and as a polishing step late in the workflow (Figure .2).
Table .2 The average and maximum purification factors of the four major chromatographic methods utilised during downstream processing as determined from a survey of the primary literature.
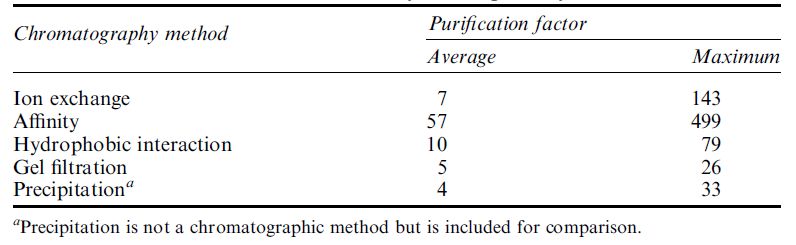
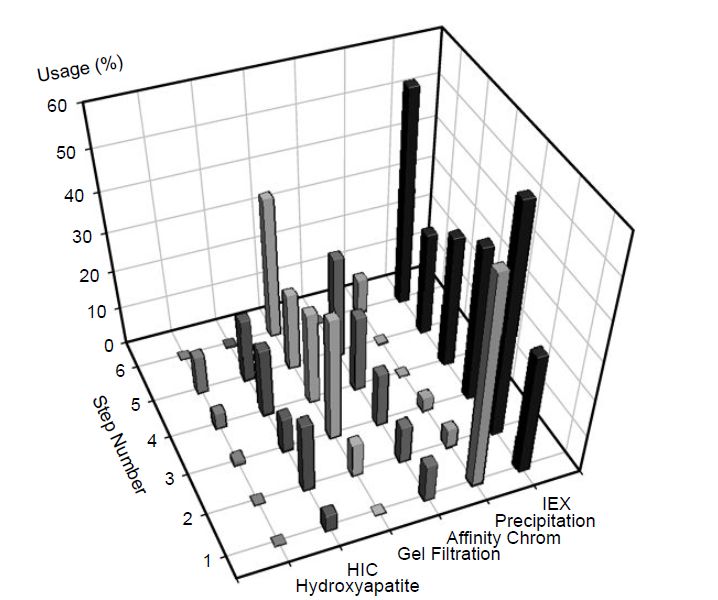
Figure .2 The use of chromatography and precipitation methods as a percentage of the total number of unit operations at a given step throughout downstream processing as determined from a survey of the primary literature. IEX, ion exchange; HIC, hydrophobic interaction chromatography.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


